FIG. 1.
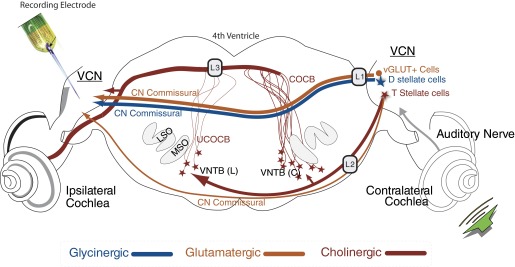
Schematic of the pathways to the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN) of the guinea pig that originate in the contralateral ear. Illustrated are: 1) the direct inhibitory glycinergic pathway via the dorsal/intermediate acoustic striae (D/IAS); 2) direct glutamatergic CN commissural projections via the D/IAS; 3) direct glutamatergic CN commissural projections via the trapezoid body (TB); or 4) cholinergic neurons of the olivocochlear bundle (OCB) that send excitatory collaterals to the VCN. Lesions of the D/IAS (L1) and TB (L2) as they exit the contralateral CN identify whether contralateral excitation is mediated by the D/IAS or the TB. L1 lesions would also disrupt glycinergic inhibition. Lesions of the OCB near the floor of the 4th ventricle (L3) elucidate the role played by the crossed and uncrossed OCB (COCB and UCOCB, respectively) (modified from de Venecia et al. 2005).
