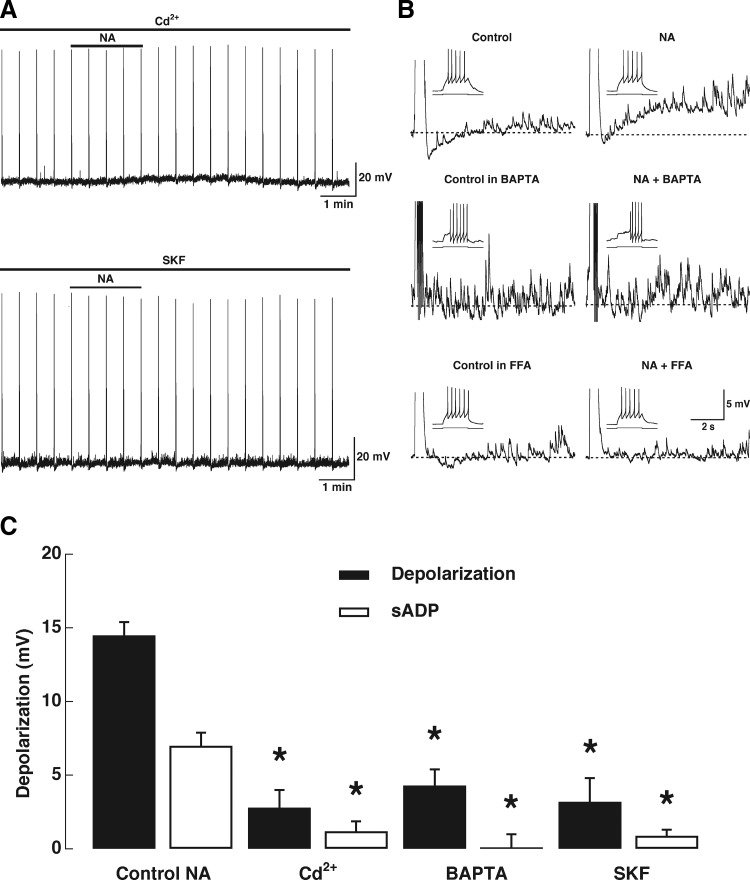
FIG. 3.
Pharmacology and Ca2+ dependence of the NA-induced afterdepolarization. A: the depolarization and ADP induced by NA (10 μM, top bar; stimulus 47 pA, 500 ms) are completely abolished in the presence of the voltage-gated Ca2+ channel blocker cadmium (Cd2+, 200 μM, top left trace). In another cell the receptor-operated Ca2+ channel blocker SKF96365 (SKF, 30 μM, bottom left trace) also completely blocked the depolarization and ADP induced by NA (10 μM, top bar; stimulus 45 pA, 500 ms). B, top right traces: control and NA-induced sADP. Middle traces: in another GC recorded with the Ca2+ chelator BAPTA, the sADP induced by NA is completely abolished. Bottom traces: the response to NA is also completely abolished in the presence of the nonselective cation channel blocker flufenamic acid (FFA, 30 μM). C: graph bar summarizing the effects of different blockers on the depolarization and sADP elicited by NA (10 μM); both the depolarization and sADP are reduced by these blockers; the asterisks indicate a significance of ≥P < 0.01 (see text).