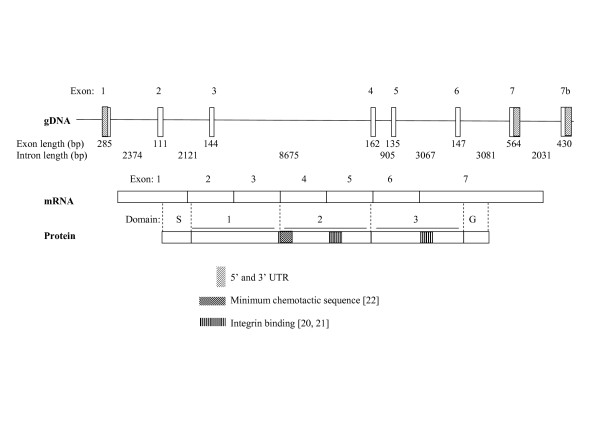
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of uPAR structure. UPAR consists of seven exons, with an alternative exon 7b previously reported [24]. The classical form is transcribed to give a three domain protein which can be membrane bound, via a GPI anchor. Domain S: Signal peptide removed during processing, Domain G: removed during processing to give GPI anchor at new C-terminus. Different regions of each domain involved in various protein-protein interactions are highlighted, which may give an indication of the functions of variant forms of the receptor. uPA binding involves residues in all three domains (see Figure 4), with key binding regions in D1 and D2 [17,19]. The minimum chemotactic sequence is located in the D1-D2 linker [22], A region implicated in binding integrins α1β3 and α5β1, aiding signalling to vitronectin, which also has chemotactic activity is located in D2 [20]. A region in D3 which binds integrin α5β1 is also highlighted [21].