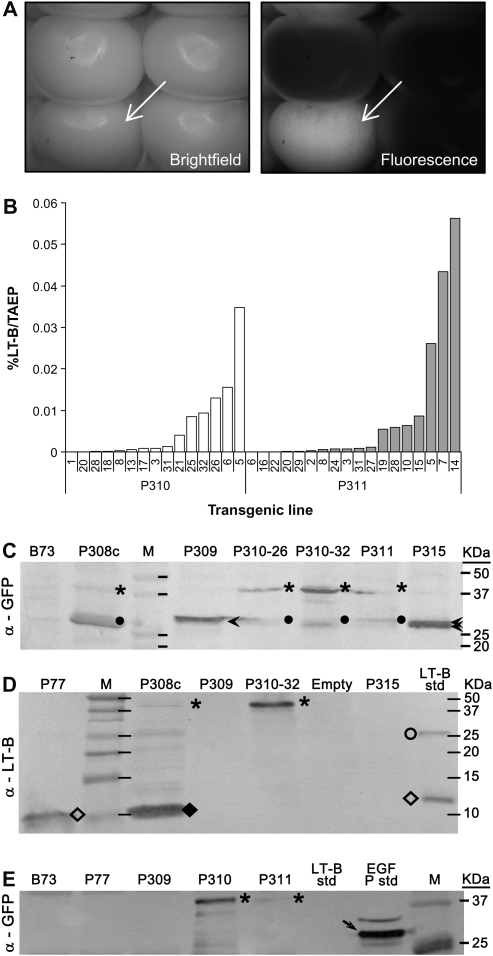
Fig. 2.
Gene expression analyses of LT-B, GFP, and LT-B::GFP fusions in transgenic maize kernels. (A) Bright field and fluorescence imaging of a representative self-pollinated ear of transgenic line P310 (Pγzein-BSP-LT-B::GFP) expressing GFP in the endosperm. A GFP-expressing kernel is marked by a white arrow. (B) LT-B levels as a percentage of total aqueous extractable protein (% LT-B/TAEP) in endosperm of P310 and P311 (Pγzein-ZSP-LT-B::GFP) kernels. Both transgenic maize carrying BSP- or ZSP-led LT-B::GFP fusion protein show the expression of functional LT-B. However, independent lines from both constructs have different levels of LT-B. (C) Western blot of TAEP extracts from transgenic callus (P308c, P35S-BSP-LT-B::GFP) and endosperms (P309, Pγzein-GFP, GFP control; P310-28, P310-32, two independent lines from P310; P311; and P315, Pγzein-BSP-GFP) using anti-GFP antibody. (D) Western blot of TAEP extracts from transgenic callus (P308c) and endosperms (P309, P310-32, and P315) using anti-LT-B antibody. (E) Western blot of immuno-precipitated samples using anti-LT-B antibody, probed with anti-GFP antibody. B73, non-transgenic maize line. P77, transgenic maize line expressing LT-B with its native bacterial signal peptide. The empty lane in (D) was a sample lost during loading. LT-B std, bacterial LT-B protein standard. EGFP std, commercial enhanced GFP standard. Arrowheads in (C), GFP. Dots in (C), possible cleavage peptides cross-react to GFP antibody. Asterisks in (C), (D), and (E), LT-B::GFP fusion. Open diamonds in (D), LT-B monomer. Closed diamond in (D), truncated LT-B::GFP fusion. Open circle in (D), LT-B multimer. Arrow in (E), commercial EGFP. Multiple EGFP bands in GFP standard may due to incomplete protein denaturation during boiling before loading.