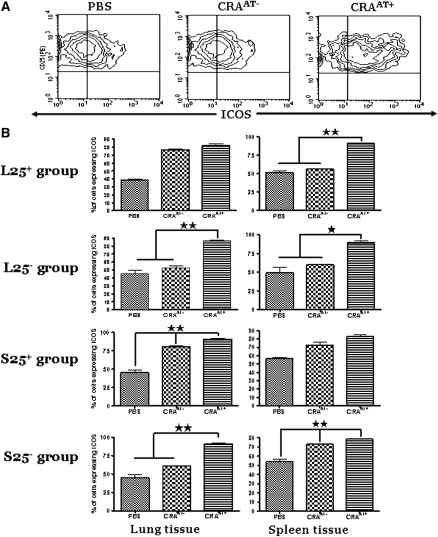
Figure 7.
The expression of inducible costimulatory molecule (ICOS) in lung and spleen CD4+CD25+ T cells post adoptive transfer. (A) Contour plots that are representative of the cells in the lung inducible CD4+CD25− T-regulatory cells (L25−) and spleen inducible CD4+CD25− T-regulatory cells (S25−) groups. ICOS was expressed at substantially high level in all cockroach-sensitized and -challenged mice with adoptive transfer (CRAAT+) groups compared with cockroach-sensitized and -challenged mice without adoptive transfer (CRAAT−) and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) control. (B) (Left panels) CD4+CD25+ T cells from lung tissue of all experiment groups. ICOS is significantly upregulated in all CRAAT+ groups compared with CRAAT− and PBS control groups with the exception of lung naturally occurring CD4+CD25− T-regulatory cells (L25+) group. The right panels are from spleen tissue of the same animals that showed high expression of ICOS in L25+ and L25− of CRAAT+ compared with low levels in CRAAT− and PBS control. *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001.