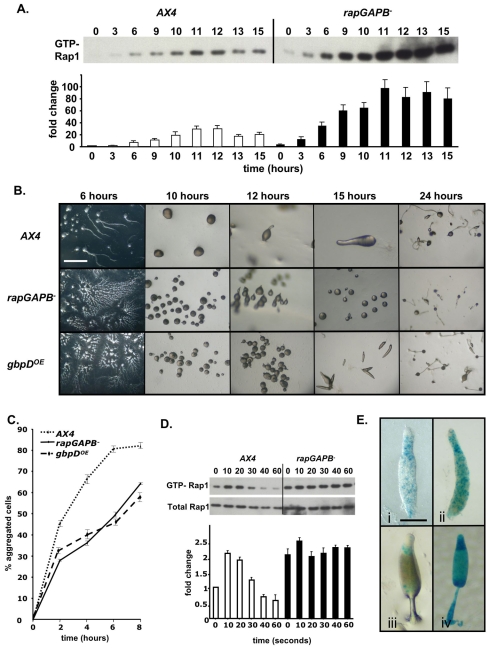
Fig. 3.
RapGAPB expression is required for developmentally regulated Rap1 activity and for normal morphogenesis. (A) Developmental regulation of activated Rap1 levels. In wild-type cells, levels of GTP-Rap1 peak after 12 hours of development before decreasing. In rapGAPB– cells, GTP-Rap1 levels are higher at all time points and do not decrease during later developmental stages. The graph shows relative amounts of GTP-Rap1 compared with levels in AX4 cells at time 0. (B) Development of wild-type AX4, rapGAPB– and gbpDOE cells. Developing rapGAPB– and gbpDOE cells both formed streams that broke up, resulting in many small mounds. rapGAPB– and gbpDOE cells formed abnormal tip mound structures. The development of rapGAPB– cells temporarily halted at the mound stage before eventually forming small culminants. The small mounds formed by the gbpDOE cells made small slugs that culminated normally to form culminants. Scale bar: 2 mm. (C) Cell-cell adhesion of streaming cells was measured by disaggregating cells and counting the number of cells that reaggregated at different time points. rapGAPB– and gbpDOE cells are less adhesive because fewer cells reaggregated at all time points. (D) cAMP-induced activation of Rap1 in 12 hour developed cells. Western blot shows levels of activated Rap1 (top panel) and total Rap1 (bottom panel). In wild-type cells, levels of active Rap1 peaked after 10 seconds of cAMP stimulation, followed by a steady decrease. In rapGAPB– cells, the level in unstimulated cells was similar to the maximal level in wild-type cells at all time points. Graph shows relative levels of GTP-Rap1 compared with that in AX4 cells at 0 seconds. (E) To determine the expression pattern of rapGAPB, the rapGAPB promoter was placed upstream of lacZ and transformed into wild-type cells. When stained for a short time, expression is enriched in the collar region of slugs (i) and in the upper and lower cups of culminants (iii). After longer periods of staining, stained cells were predominantly found in the collar region, but also found scattered throughout the entire slug (ii) and in the apical tip, upper and lower cups and spores of culminants (iv). Scale bar: 1 mm.