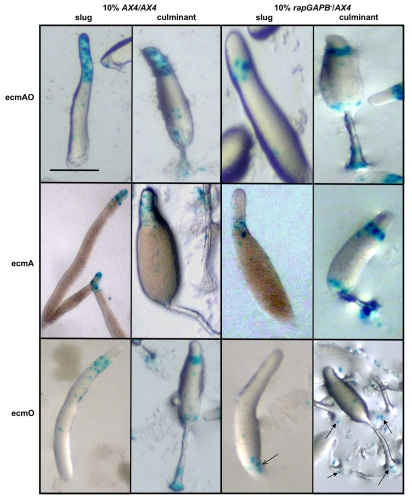
Fig. 7.
rapGAPB– mutant cells show defects in ecmAO-lacZ, ecmA-lacZ and ecmO-lacZ expression in chimeras. AX4 or rapGAPB– cells were transformed with cell-specific markers. 10% of cells expressing these markers were mixed in chimeras with 90% unlabeled cells and developed. Expression of the markers was observed at both the slug and early culminant stages of development. Clear defects were observed in the expression of ecmAO-lacZ, ecmA-lacZ and ecmO-lacZ in chimeras. When AX4 cells expressing ecmAO-lacZ were mixed with AX4 cells, ecmAO expression was found in the entire prestalk region of slugs and in the apical tip, upper cup and lower cup of culminants. However, when rapGAPB– cells expressing ecmAO-lacZ were mixed with AX4 cells, ecmAO expression was absent from the tip of slugs and only present in the collar region. In addition, in the culminant expression was absent from the apical tip. When AX4 cells expressing ecmA-lacZ were mixed with AX4 cells, ecmA expression was found in tip of slugs and in the apical tip and stalk of culminants. However, when rapGAPB– cells expressing ecmA-lacZ were mixed with AX4 cells, ecmA expression was absent from the tip of slugs and instead present in the collar region. In addition, expression was absent from the apical tip and found instead in the upper and lower cups of culminants. When AX4 cells expressing ecmO-lacZ were mixed with AX4 cells, ecmO expression was found in the collar region of slugs and in the upper cup and lower cups of culminants. However, when rapGAPB– cells expressing ecmO-lacZ were mixed with AX4 cells, ecmO expression was largely found at the rear of the slug and in the slime trail (open arrow). In addition, expressing cells were found mainly in the basal disk of the culminant and scattered on the agar (filled arrows). Scale bar: 1 mm.