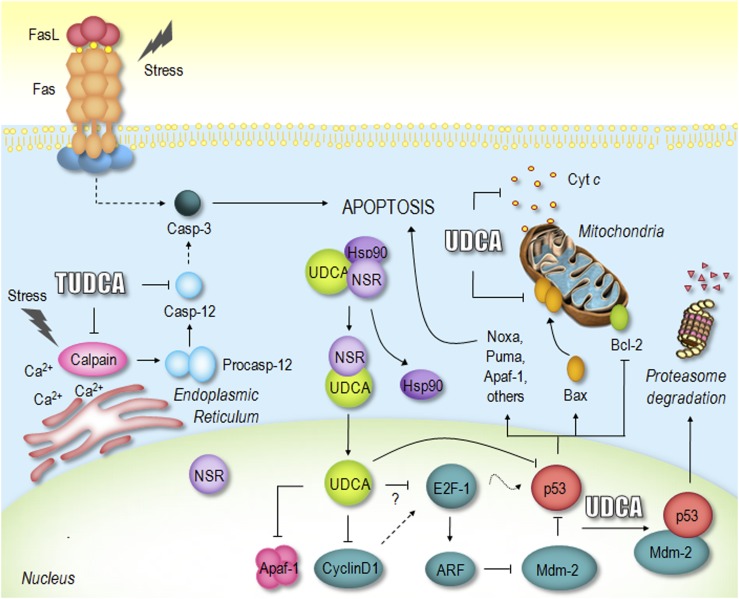
Fig. 3.
Proposed mechanisms of UDCA and TUDCA inhibition of apoptosis. UDCA negatively modulates the mitochondrial pathway by inhibiting Bax translocation, ROS formation, cytochrome c release, and caspase-3 activation. UDCA can also interfere with the death receptor pathway, inhibiting caspase-3 activation. Moreover, TUDCA inhibits apoptosis associated with ER stress by modulating intracellular calcium levels and inhibiting calpain and caspase-12 activation. Importantly, UDCA interacts with NSR, leading to NSR/hsp90 dissociation and nuclear translocation of the UDCA/NSR complex. Once in the nucleus, UDCA modulates the E2F-1/p53/Bax pathway, thus preventing apoptosis. Finally, UDCA downregulates cyclin D1 and Apaf-1, further inhibiting the mitochondrial apoptotic cascade. See text for more complete description. Cyt c, cytochrome c; Hsp90, heat shock protein 90.