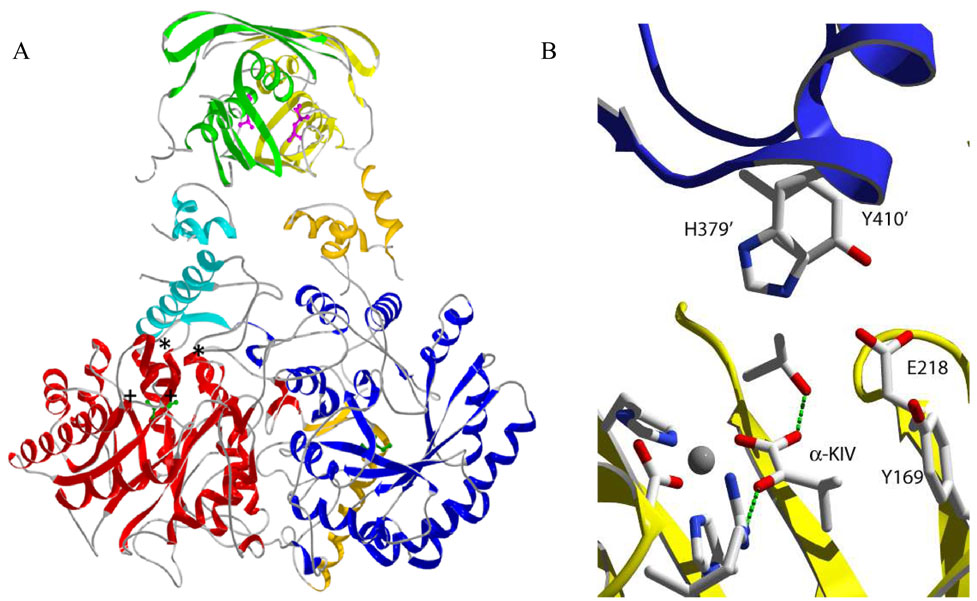
Figure 1.
Ribbon drawing of the three-dimensional structure of α-isopropylmalate synthase from M. tuberculosis. A. Domains colored red/blue, orange/cyan, and yellow/green correspond to the catalytic, linking, and regulatory domain, respectively, of each monomer. L-leucine is shown in purple in the regulatory domain. The substrate (α-KIV) is shown in green to denote the active site. The general location of substituted residues in this study are denoted by (*) for residues in the linker domain and by (+) for residues in the catalytic domain. B. Detailed rendering of residues on monomer A (yellow) and monomer B (purple and prime numbering) selected for mutational analysis. Residues involved in metal binding and α-KIV binding are shown as well. All three-dimensional structures were created with SwissPDB Viewer and rendered with POVRAY 3.5.