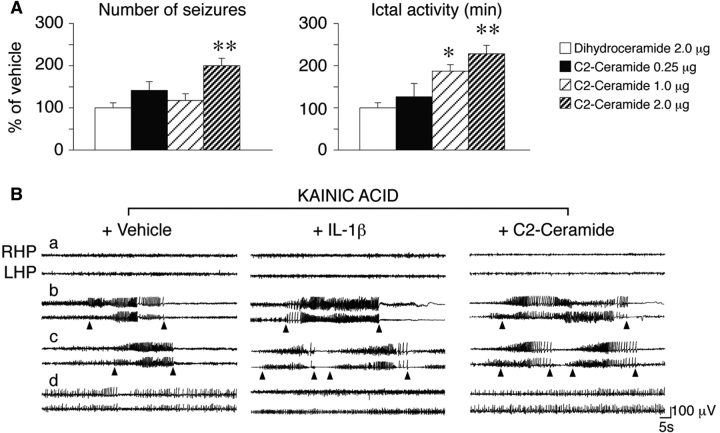
Fig. 2.
Effect of C2-ceramide on seizures. (A) Bargrams represent the mean ± SE (n = 12). Dihydroceramide, the inactive analogue of ceramide, (2 μg/0.5 µl) or C2-ceramide (the cell-permeable analogue of ceramide; 0.25–1.0–2.0 μg/0.5 μl) were injected intrahippocampally, 10 min before kainic acid. Significant increases in seizure parameters were observed at 1 and 2 µg C2-ceramide. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 versus dihydroceramide by one way ANOVA followed by Tukey test. (B) Representative EEG tracings of freely moving C57BL6 mice injected unilaterally in the hippocampus with kainic acid ± IL-1β (1 ng/0.5 μl) or C2-ceramide (2 μg/0.5 µl). Treatments or vehicles were given 10 min before kainic acid. (a) Baseline recording before kainic acid injection; arrowheads in (b) and (c) include representative ictal episodes recorded in the EEG during 90 min after kainic acid injection ± IL-1β or C2-ceramide; tracings in (d) depict spiking activity in the EEG after termination of seizures. Either IL-1β or C2-ceramide alone did not induce seizures. RHP and LHP are right and left (injected) hippocampus, respectively.