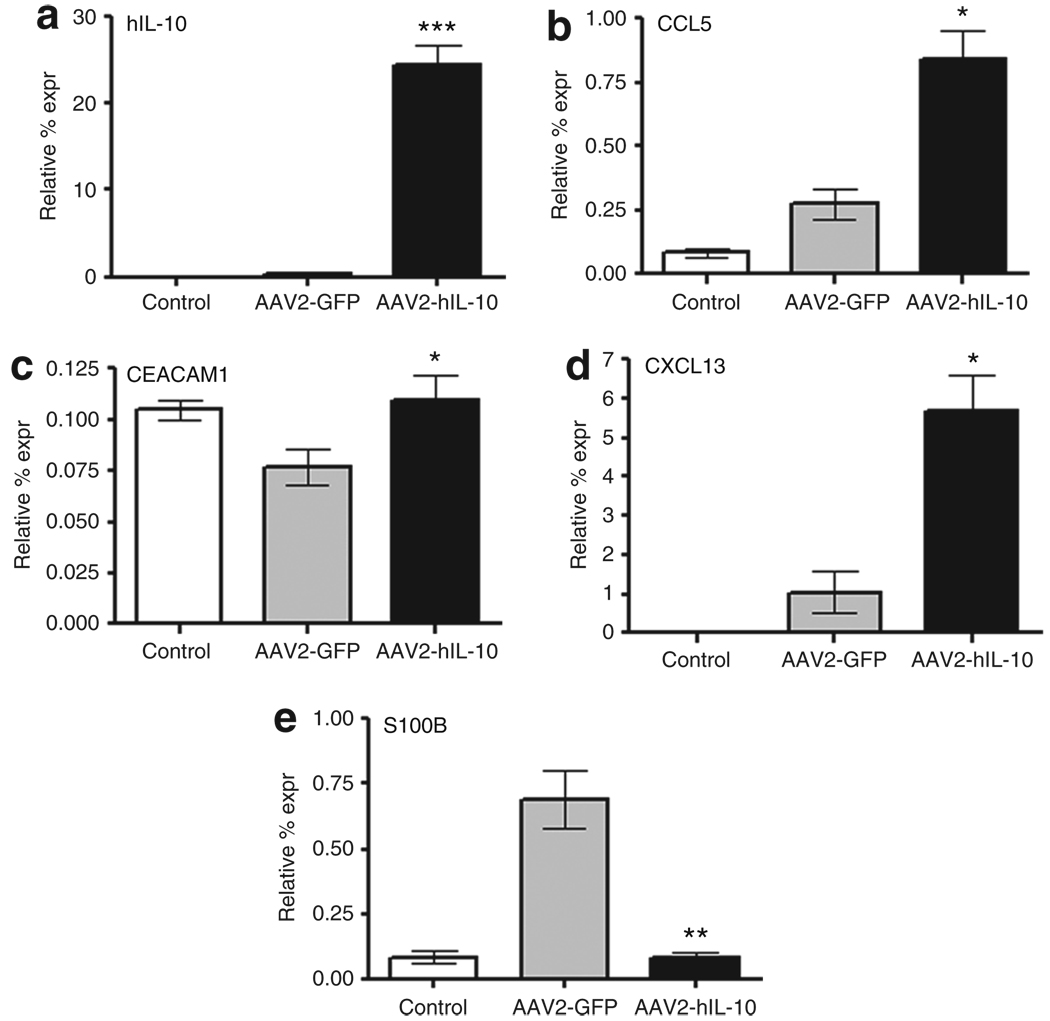
Figure 7. Acute changes in gene expression induced by 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) and modulation by the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 (IL-10).
(a) Human IL-10 (hIL-10), (b) CCL5, (c) CEACAM1, (d) CXCL13, and (e) S100B. Rats were infused with AAV2-GFP or AAV2-hIL-10 (n = 4/group). Three days later, 6-OHDA was infused. Striata (data shown for right side) were collected 3 days later. Control animals did not receive any infusions. The data are expressed as mean relative percentage expression (expr) values; normalized to the housekeeping gene for rat glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Statistical differences were measured using t-tests *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005 for AAV2-hIL-10/6-OHDA rats as compared to control transgene 6-OHDA rats. AAV2, adeno-associated virus type-2; CCL5, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5; CEACAM1, carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1; CXCL13, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 13; GFP, green fluorescent protein; S100B, S100 calcium-binding protein B.