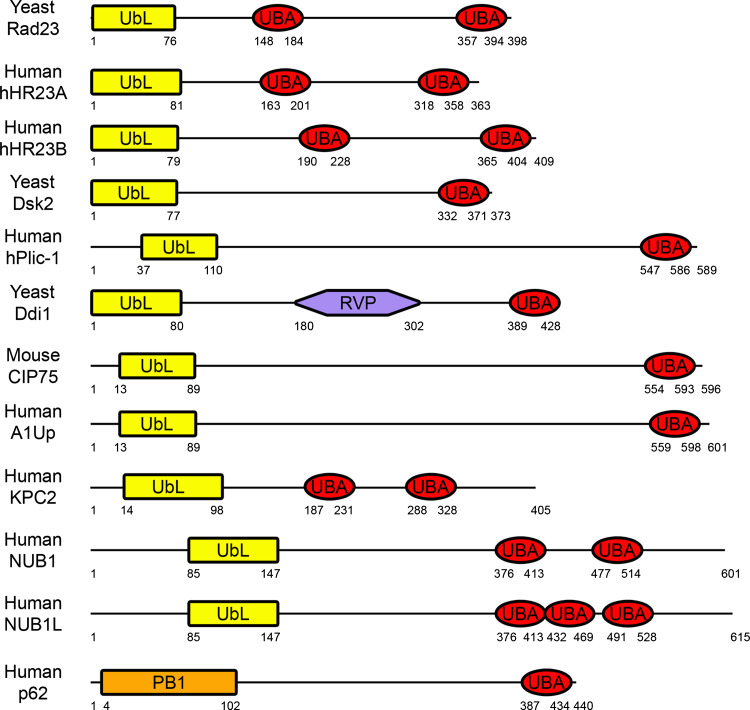
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of UbL–UBA domain-containing proteins. The domain structures of yeast Rad23 (accession number NP_010877), human hHR23A (NP_005044) and hHR23B (NP_002865), yeast Dsk2 (P48510), human hPlic-1 (Ubiquilin) (AAD49751), yeast Ddi1 (NP_011070), mouse CIP75 (UBIN) (NP_277068), human A1Up (NP_064516), human KPC2 (NP_057256), human NUB1 (NP_057202) and NUB1L (AAO14547), and human p62 (NP_003891) are shown. The UbL–UBA family of proteins contains an N-terminal UbL domain (or the structurally similar PB1 domain for p62), one or more C-terminal UBA domain(s), and a variable central region (yeast Ddi1 contains a central RVP domain). For family members with multiple UBA domains, the most N-terminal UBA domain is referred to as UBA1 in the text, and additional UBA domains are referred to as UBA2 and UBA3