Figure 3.
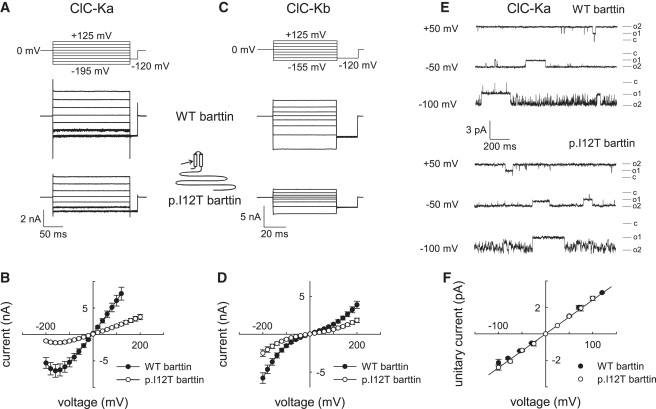
Functional Consequences of p.I12T on ClC-K/Barttin Channel Activity
(A–D) Representative recordings and current-voltage relationships of macroscopic currents from HEK293T cells coexpressing ClC-Ka (A and B) or ClC-Kb (C and D) and wild-type (WT) or p.I12T barttin with standard internal and external solutions. Whole-cell and single-channel patch-clamp recordings were performed with an Axopatch 200B amplifier (Molecular Devices).10,17 The extracellular solution contained 140 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, and 5 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), whereas the intracellular solution contained 120 mM NaCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 5 mM EGTA, and 10 mM HEPES (pH 7.4). The voltage dependence of instantaneous current amplitudes was determined with voltage steps (8–10 ms) from a holding potential of 0 mV so that potentials between −200 to +200 mV could be tested. Data points represent means ± SEM from between 16 and 26 cells.
(E and F) Representative single-channel recordings (E) and unitary current-voltage relationships (F) of ClC-Ka/barttin channels for WT or p.I12T barttin. Single-channel recordings were either performed in the inside-out configuration, with pipettes containing the standard extracellular solution and cells bathed in the standard intracellular solution, or in the cell-attached configuration with cells bathed in the standard extracellular solution and the pipettes containing a modified bath solution with 140 mM KCl, 4 mM NaCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, and 5 mM HEPES (pH 7.4). Currents were sampled at 50 kHz and filtered at 500–1000 Hz. Because of the high open probability of ClC-Ka/barttin channels, unitary current amplitudes were manually determined from channel closures that exceeded 5 ms. Data points represent means ± SEM from three to ten measurements.
