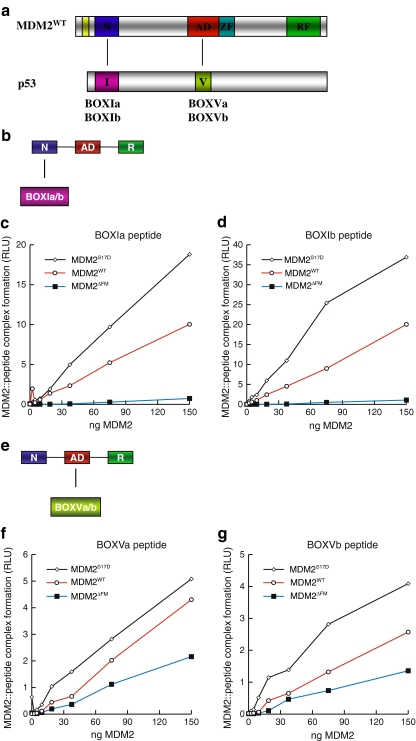
Fig. 6.
Phospho-mimetic substitution in the MDM2 lid motif enhances MDM2 binding activity for BOX-I and BOX-V peptide ligands. a The domain structure of MDM2 minidomains, relative to p53 minidomains containing the BOX-I and BOX-V docking regions is highlighted. The panel highlights (a) an interaction between the N-terminal MDM2 domain (N) and the p53 BOX-I motif (I) and (b) an interaction between the acid domain of MDM2 (AD) and the BOX-V motif of p53 (V). b The assay was designed to measure the interaction between the N-terminal domain of full-length MDM2 and the BOX-I-derived p53 peptide. c and d MDM2S17D has an enhanced binding activity for the BOX-I domain of p53. wt-MDM2, MDM2ΔLID, or MDM2S17D proteins were titrated into reaction buffer and incubated onto the solid phase containing BOX-I a peptide (left panel) and BOX-I b peptide (right panel). The amount of MDM2 bound stably to the p53 peptides was quantified using an MDM2 monoclonal antibody. The stability of the MDM2:p53 complex is depicted in relative light units. e The assay was designed to measure the interaction between the central acidic domain of full-length MDM2 and the BOX-V-derived peptides. f and g MDM2S17D has an enhanced binding activity for the BOX-V domain of p53. wt-MDM2, MDM2ΔLID, or MDM2S17D proteins were titrated into reaction buffer and incubated onto the solid phase containing BOX-V a peptide (left panel) and BOX-V b peptide (right panel). The amount of MDM2 bound stably to the p53 peptides was quantified using an MDM2 monoclonal antibody. The stability of the MDM2:p53 complex is depicted in relative light units