Fig. 8.
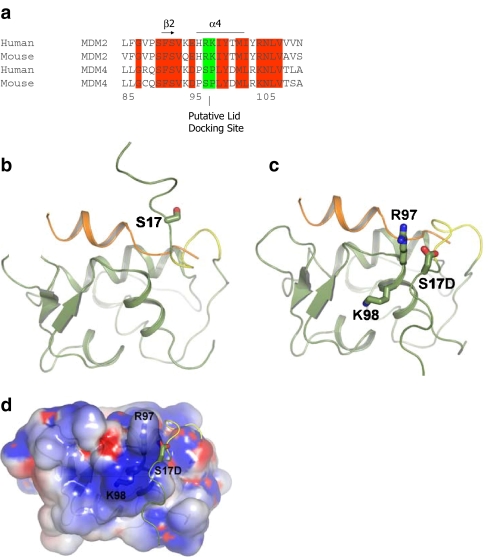
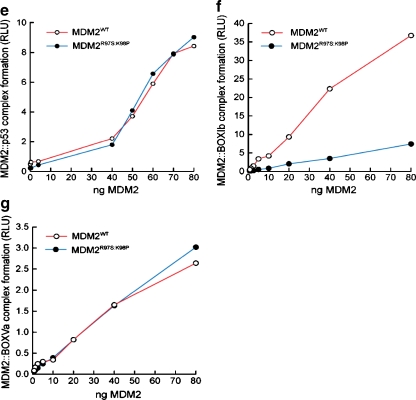
A model of lid function through stabilization of the phospho-mimetic motif on the surface of MDM2. a Multiple sequence alignment of MDM2 and MDM4 highlighting the evolutionary divergence between MDM2 and MDM4 at the potential pseudo-substrate motif basic docking site for acidic residues (i.e., Asp, phosphate) at amino acid residues 97–98. b The C-terminal region of the pseudo-substrate domain (residues 18–24; colored yellow) can have helical character and occupy the shallow end of the hydrophobic binding pocket as reported previously [25]. The p53 peptide from PDB structure 1YCR [20] is shown for comparison (colored orange). The N-terminal p53 peptide sequence and the lid cannot occupy the hydrophobic pocket simultaneously. c The pseudo-substrate motif can also exist displaced from the binding pocket with Ser17 (S17D mutation shown for illustration) in proximity to a basic region (see d) at the N-terminal of helix α2′ composed of Arg97/Lys98. Based on this, it is postulated that the S17D (mimicking phosphorylation of Ser17) mutation could stabilize the N-terminal domain of MDM2 in a conformation primed for p53 binding by forming electrostatic interactions with residues Arg97/Lys98. e–g Effects of Arg97/Lys98 mutation on wild-type MDM2 activity. e MDM2 codon 97–98 residue mutation to the MDM4 equivalent does not destabilize the MDM2:p53 tetramer complex. Increasing amounts of the indicated MDM2 protein (wt-MDM2 or MDM2R97S:K98P) were titrated into reactions where fixed amounts of tetrameric p53 were on solid phase as described previously above. The extent of MDM2 binding was quantified using an anti-MDM2 monoclonal antibody and binding stability depicted using enhanced chemiluminescence in relative light units (RLU). f The effects of MDM2 codon 97–98 residue mutation to the MDM4 equivalent on MDM2:BOX-I peptide complex stability. Increasing amounts of MDM2 protein (wt-MDM2 or the double mutant MDM2R97S:K98P) were titrated into reactions with fixed amounts of the BOX-I peptide on solid phase, as described previously above. The extent of MDM2 binding was quantified using an anti-MDM2 monoclonal antibody and binding stability depicted using enhanced chemiluminescence in relative light units (RLU). g The effects of MDM2 codon 97–98 residue mutation to the MDM4 equivalent on MDM2:BOX-V peptide complex stability. Increasing amounts of MDM2 protein (wt-MDM2 or the double mutant MDM2R97S:K98P) were titrated into reactions with fixed amounts of the BOX-V peptide on solid phase, as described previously above. The extent of MDM2 binding was quantified using an anti-MDM2 monoclonal antibody and binding stability depicted using enhanced chemiluminescence in relative light units (RLU)