Fig. 9.
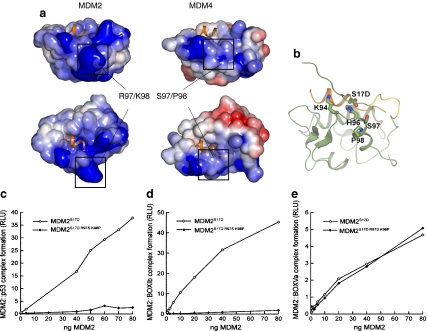
Inactivation of MDM2S17D by mutation of surface basic residues of MDM2. a Electrostatic potential mapped onto the solvent accessible surface. Positive- and negative-charged regions colored blue and red, respectively. Alignment figure generated with ESPript [14]. Structural figures generated with PyMol (www.pymol.org). The electrostatic calculations were performed with APBS [3] and highlighted is (left) wild-type MDM2 and (right) MDM2 with R97/K98 residues substituted with the S97/P98 MDM4 residues. b When the basic patch on MDM2 is mutated to Ser97/Pro98, the phospho-mimetic pseudo-substrate motif may bind other basic regions of the MDM2 surface such as Lys94/His96, which line the hydrophobic binding pocket and explain why the MDM2 triple mutant (MDM2S17D:R97S:K98P) binds p53 with a substantially lower activity than does the MDM2 double mutant (MDM2R97S:K98P; see c–e). c MDM2 codon 97–98 residue mutation to the MDM4 equivalent inactivates MDM2S17D as a p53 binding protein. Increasing amounts of the indicated MDM2 protein (MDM2S17D or the triple mutant MDM2S17D:R97S:K98P) were titrated into reactions where fixed amounts of tetrameric p53 were on solid phase as described previously above. The extent of MDM2 binding was quantified using an anti-MDM2 monoclonal antibody and binding stability depicted using enhanced chemiluminescence in relative light units (RLU). d The effects of MDM2 codon 97–98 residue mutation to the MDM4 equivalent on MDM2S17D:BOX-I peptide complex stability. Increasing amounts of MDM2 protein (MDM2S17D or the triple mutant MDM2S17D:R97S:K98P) were titrated into reactions with fixed amounts of the BOX-I peptide on solid phase, as described previously above. The extent of MDM2 binding was quantified using an anti-MDM2 monoclonal antibody and binding stability depicted using enhanced chemiluminescence in relative light units (RLU). e The effects of MDM2 codon 97–98 residue mutation to the MDM4 equivalent on MDM2S17D:BOX-V peptide complex stability. Increasing amounts of MDM2 protein (MDM2S17D or the triple mutant MDM2S17D:R97S:K98P) were titrated into reactions with fixed amounts of the BOX-V peptide on solid phase, as described previously above. The extent of MDM2 binding was quantified using an anti-MDM2 monoclonal antibody and binding stability depicted using enhanced chemiluminescence in relative light units (RLU)