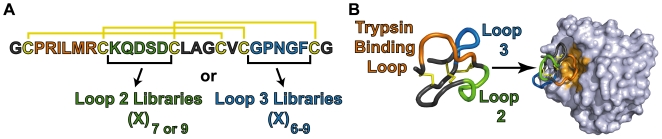
Figure 1. Schematic for interrogating the tolerance of sequence diversity in knottin loops.
(A) Six libraries of loop-substituted knottin variants were designed based on the wild-type sequence of EETI. Libraries were created by replacing cysteine-flanked loop 2 (green) or loop 3 (blue) sequences with peptides of randomized amino acids (X) and varying lengths (n). The trypsin binding loop (orange) was not replaced, but instead used as a handle to evaluate the proper folding of EETI loop-substituted clones. Disulfide bonds are shown in yellow. (B) The binding interaction between trypsin (light grey) and EETI (PDB 2eti and 1h9h) is mediated through the trypsin binding loop, and is dependent on the correct formation of all three disulfide bonds. This interaction was exploited for high-throughput isolation of properly folded EETI loop-substituted variants.