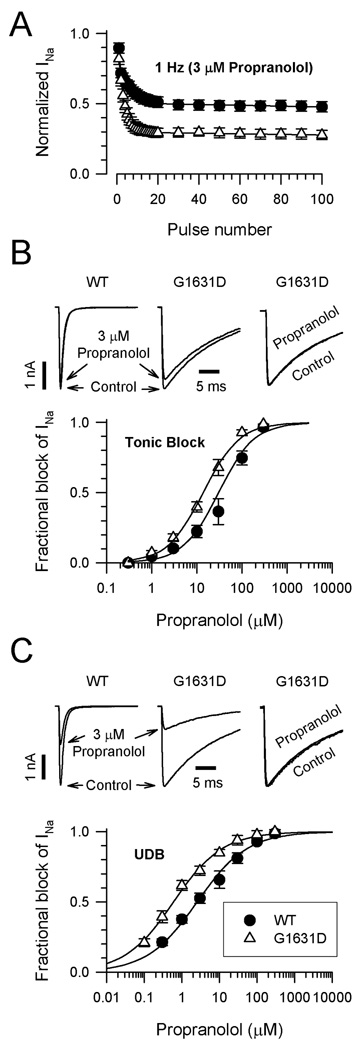
Figure 7.
Effects of propranolol on WT and G1631D. (A) Propranolol (3µM) block of WT (n=5) and G1631D (n=4) during a 1Hz train of depolarizing pulses to −10mV from a holding potential of −120mV. (B) Tonic propranolol block of WT and G1631D. Upper traces (left, middle) illustrate the effects of 3µM propranolol during a single depolarizing voltage step to −10mV. Normalized traces (right) recorded in the absence (control) or presence of drug illustrate the effect of propranolol on the inactivation time course. The plot illustrates the concentration-response relationships for tonic block by propranolol (each data point represents the mean of 4–11 cells). (C) Use-dependent propranolol block of WT and G1631D. Upper traces (left, middle) illustrate the steady state effects of 3µM propranolol during a 1Hz pulse train. Normalized traces (right) recorded in the absence (control) or presence of drug (100th pulse) illustrate the effect of propranolol on the inactivation time course. Time constants in the absence of drug were: τ1=7.8±0.5ms, τ2=19.5±0.7ms, n=4; and in the presence of 3µM propranolol: τ1=6.9±1.1ms, τ2=18.1±1.0ms n=4 (no significant differences in τ1 or τ2). The plot illustrates the concentration-response relationships for use-dependent block by propranolol (each data point represents the mean of 4–11 cells). The lines in B and C were fit to the data according to the Hill equation.