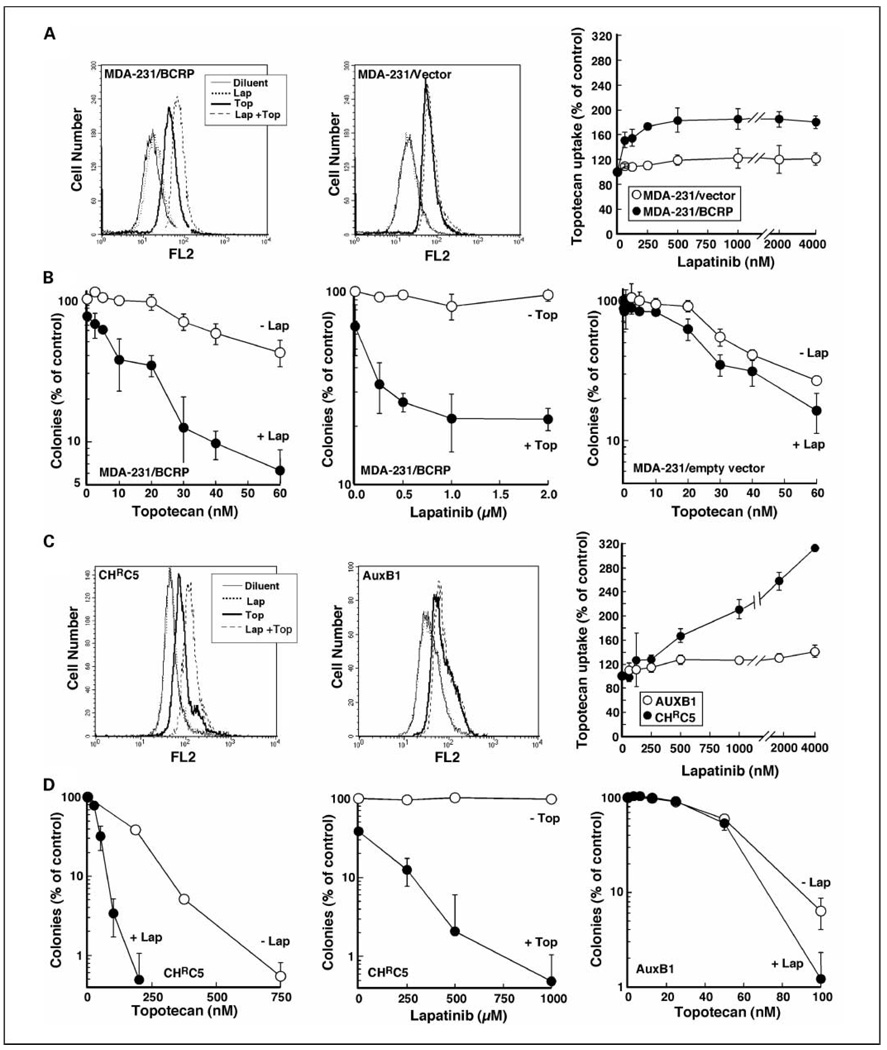
Fig. 1.
Lapatinib enhances topotecan uptake and cytotoxicity in tumor cells overexpressing BCRP or Pgp. A and C, left, after cells that overexpress BCRP (MDA-MB-231/BCRP) or Pgp (CHRC5) were incubated with DMSO,1 µmol/L lapatinib (Lap) in DMSO, topotecan (Top) in DMSO, or lapatinib and topotecan (Lap + Top) simultaneously for 20 to 30 min, topotecan accumulation was assayed by flow microfluorimetry. All samples contained 0.2% (v/v) DMSO. Middle, cells that express lower endogenous levels of BCRP (MDA-MB-231/empty vector) or Pgp (AuxB1) were used as controls. Right, summary of results as a function of lapatinib concentration. The values shown were corrected by subtracting the minimal fluorescence attributable to lapatinib at the corresponding concentrations. Points, mean of three independent experiments; bars, SD. B and D, left, after treatment for 24 h with the indicated concentration of topotecan or diluent in the presence or absence of1 µmol/L lapatinib, cells were washed and allowed to form colonies. Middle, ABC transporter-overexpressing cells were treated for 24 h with varying concentrations of lapatinib in the presence or absence of 40 nmol/L topotecan (B, middle) or 200 nmol/L topotecan (D, middle) and then assayed for colony formation. Right, MDA-MB-231/empty vector (B, right) orAuxB1cells (D, right) were treated for 24 h with the indicated concentration of topotecan or diluent in the presence or absence of 1 µmol/L lapatinib, washed, and allowed to form colonies. Points, mean of triplicate plates; bars, SD. Similar results were observed in three independent experiments.