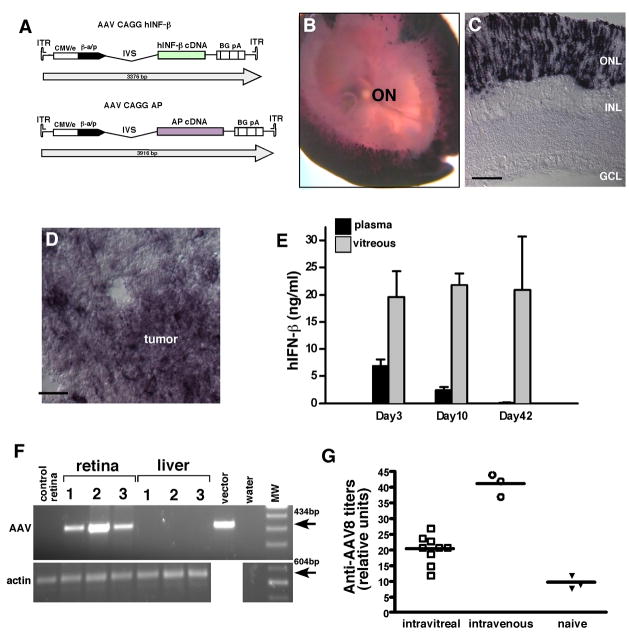
Fig 3. AAV infection and spread following intravitreal injection.
The human placental alkaline phosphatase (AP) gene and the human IFN-β genes were cloned into the AAV vector to generate AAV-AP and AAV- IFN-β vectors (A). Vitreal injection led to efficient infection of the photoreceptor layer across the entire retina as shown in whole mount AP stained retinae (B) and cryosections (C). In tumor bearing animals, the AAV-AP virus also infected the human Y79 retinoblastoma cells (D). The vitreal and plasma levels of IFN-β were measured following intravitreal injection of AAV- IFN-β 3, 10 and 42 days after injection (E). There was no evidence of viral spread outside of the eye as measured by by PCR analysis of liver or other tissues (F). As additional evidence for minimal AAV spread outside of the eye following an intravitreal injection, an ELISA was performed to measure anti-AAV8 antibody titer in naieve rats, those that received an intravitreal injection and rats that received an intravenous injection of AAV8 (G).