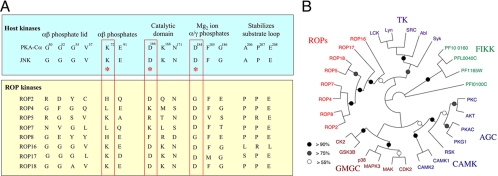
FIG. 3.
Divergence of ROP2 family members and degeneracy in the conserved kinase domains. (A) Alignment of several mammalian kinases (PKA-Cα and Jun N-terminal protein kinase [JNK]) showing conservation of key residues implicated in binding to ATP and in catalysis. The catalytic triad is boxed in red. While a majority of ROP2 family members are divergent and are predicted to be inactive, ROP16, ROP17, and ROP18 conserve the key residues associated with activity. (B) Phylogenetic tree showing the relationship between ROP kinases, FIKK kinases from P. falciparum, and major families of human kinases. TK, tyrosine kinases; AGC, cAMP-regulated kinase, c-GMP regulated kinase, and PKC; CAMK, calcium-regulated kinases; GMCC, cyclin-dependent, mitogen-activated, and casein kinases. (Reproduced from reference 36.)