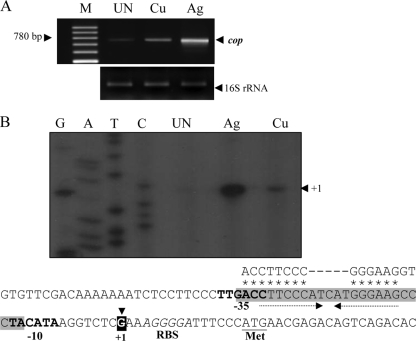
FIG. 2.
Transcription and promoter analysis of copARZ. (A) RT-PCR analysis of copARZ was carried out with primers BT1830 and BT1683. Total RNA was extracted from NTL4 cultures cultivated under uninduced conditions (UN) and after induction with 25 μM AgNO3 (Ag) or 500 μM CuSO4 (Cu). The RT-PCR products were separated by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. M, 100-bp molecular weight markers (Fermentas, Canada). (B) Primer extension experiments were performed using RNA isolated from uninduced (UN), AgNO3-induced (Ag), or CuSO4-induced (Cu) cultures of A. tumefaciens NTL4 with 32P-labeled primer BT1968. Extension products were sized on sequencing gels next to DNA sequence ladders (G, A, T, and C) generated using pGEM-3Zf(+) as the template and labeled forward primer pUC/M13. The arrowhead indicates the putative transcription start site (position +1). Putative −35 and −10 motifs are in boldface type. The ribosome binding site (RBS) and start codon (ATG) are in italic type and underlined, respectively. Arrows represent inverted repeat sequences. The consensus sequence of the CueR binding site (37) is aligned above the sequence line in corresponding letters, and the homologous nucleotides are marked by asterisks. The gray shaded box indicates the CopR binding box according to DNase I footprinting assays.