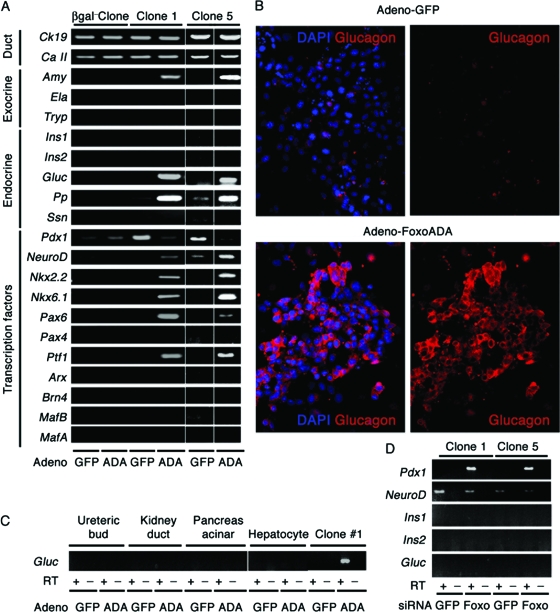
FIG. 10.
Induction of glucagon expression by FoxO1 gain of function in clonal duct cultures. (A) mRNA expression analysis of a β-gal-negative clone and two representative β-gal-positive (FoxO1+ Ins−) clones (1 and 5) transduced with adenovirus expressing constitutively active FoxO1ADA or GFP. Ck19, cytokeratin 19; Ca II, carbonic anhydrase II; Amy, amylase; Ela, elastase; Try, trypsin; Ins1, insulin 1; Ins2, insulin 2; Gluc, glucagon; Ssn, somatostatin. (B) Glucagon immunocytochemistry (red) in cells transduced with adenovirus encoding FoxO1ADA or GFP. (C) We transduced clone 1 and control cells, including embryonic UB cells, M-1 cells, TGP47 cells, and SV40-transformed hepatocytes, with FoxO1ADA adenovirus. After isolating mRNA, we performed semiquantitative RT-PCR with primers for glucagon. (D) Expression of Pdx1, NeuroD, Ins1, Ins2, and Gluc in clones 1 and 5 following transfection of FoxO1 or control siRNA. The RT-PCRs for Pdx1 and NeuroD were carried out for 25 cycles, and Pdx1 was undetectable in control samples under these conditions.