FIG. 2.
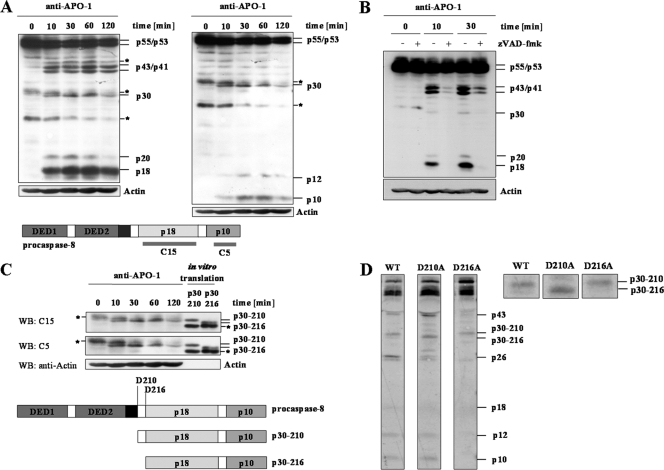
p30 comprises the C terminus of procaspase-8. (A) SKW6.4 cells were stimulated with anti-APO-1 MAb for different times, and procaspase-8 cleavage was analyzed by Western blotting with the anti-caspase-8 MAbs C15 (left panel) or C5 (right panel) and the antiactin MAb. (*, unspecific band). (B) SKW6.4 cells were pretreated with 20 μM of zVAD-fmk and stimulated with anti-APO-1 MAb for different times. Procaspase-8 processing was analyzed by Western blotting using the anti-caspase-8 MAb C15. Antiactin Western blotting was used as a loading control (*, unspecific band). (C) Lower part: scheme of procaspase-8a/b and the putative structures of p30 resulting from cleavage at Asp210 and Asp216. Upper part: in vitro-translated p30-216 and p30-210 were loaded on the same gel as total cellular lysates of CD95-stimulated SKW6.4 cells. Western blotting (WB) was performed using the anti-caspase-8 MAbs C15 and C5. Antiactin Western blotting was used as a loading control (*, unspecific band). (D) Wild-type (WT) procaspase-8a and mutants of procaspase-8a (D210A and D216A) were translated in vitro in the presence of [35S]methionine and added to the CD95 DISCs isolated from SKW6.4 cells. Processing of procaspase-8a by the DISCs was monitored by 35S autoradiography. The enlargement of the 30-kDa region is presented at the right side of the figure.