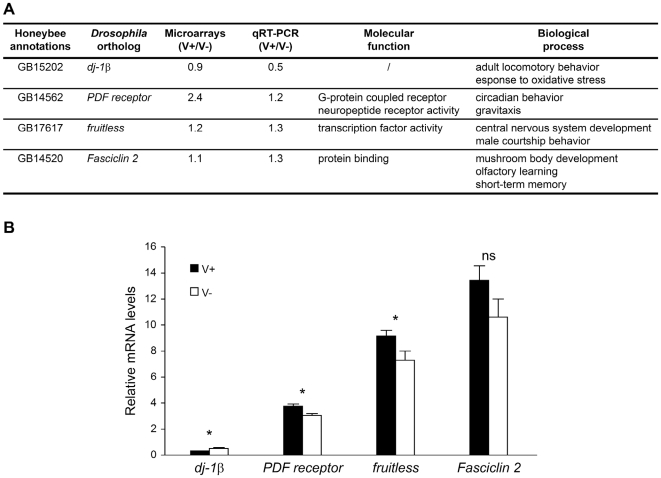
Figure 1. Genes differentially expressed between vibration signal performers and non-performers.
A. Description of the 4 genes analyzed, chosen from among the 918 differentially expressed between V+ and V− bees functions based on Gene Ontology information for Drosophila melanogaster orthologs. B. Brain mRNA levels for these 4 genes. n = 7 individuals/group. qPCR data were normalized to expression levels of eIF3-S8. Significant differences were determined using a Wilcoxon signed rank test (*p<0.05, ns = not significant). Means±s.e. are shown. The four genes were chosen because of their functions in Drosophila, which can be linked plausibly to vibratory communication signal in bees. Vibrating bees display a high rhythmic locomotion rate, and dj-1β, PDF receptor and fruitless are involved in locomotory and rhythmic behavior [31]–[35]. They also need to assess and memorize the colony needs and Fasciclin 2 is involved in olfactory learning and mushroom body development [36], [37]. Differences in expression were detected in 3 out of 4 genes with qPCR; these results are not inconsistent with expectations from the False Discovery Rate used in this study for analysis of microarray results.