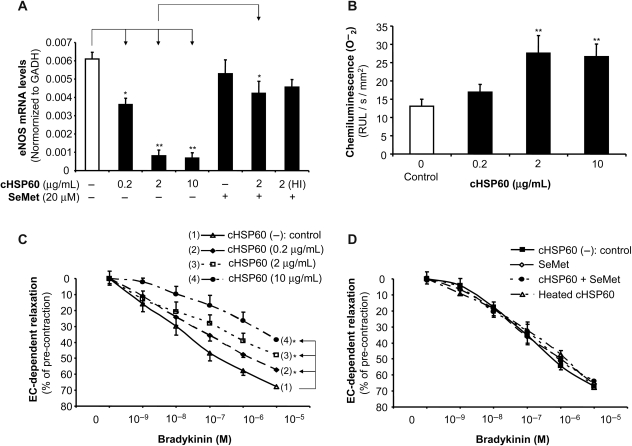
Figure 6.
Effects of cHSP60 on eNOS expression, superoxide anion production, and vasomotor functions in porcine coronary arteries. Porcine right coronary artery rings were cultured with cHSP60 (0.2, 2, or 10 µg/mL), with or without antioxidant SeMet (20 µM) for 24 h. (A) The eNOS mRNA levels were determined by real-time PCR. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, n = 4, t-test. (B) The superoxide anion (O−2) levels were determined by lucigenin-enhanced chemiluminescence assay. The data were normalized with area (mm2) of the ring and are expressed as relative light units (RLU/s/mm2). **P < 0.05, n = 6, t-test. (C) Vasomotor function was determined by myograph analysis for cHSP60 (0.2, 2, or 10 µg/mL) treatment group. After cHSP60 treatment, porcine right coronary artery rings were pre-contracted with thromboxane A2 analogue U46619 (3 × 10−8 M) and then subjected to endothelium-dependent relaxation by adding a series of concentrations of bradykinin (10−9–10−5 M). *P < 0.05, n = 10, ANOVA. (D) Vasomotor functions determined by myograph analysis for HI-cHSP60, SeMet, and SeMet plus cHSP60 treatment groups. The endothelium-dependent relaxation in response to a series of concentrations of bradykinin in each treatment group did not show any change compared with untreated controls.