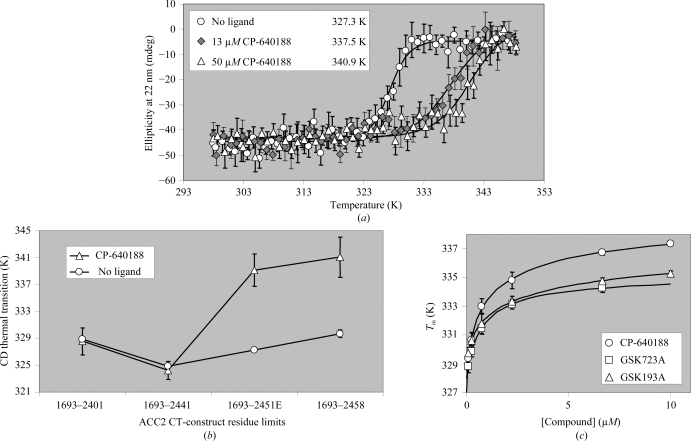
Figure 3.
Thermal denaturation is influenced by ligand binding to human ACC2 CT domain. (a) A reproducible and saturable increase in the melting temperature of ACC2 (1693–2451) (circles) is observed when 13 µM (gray diamonds) and 50 µM (triangles) CP-640188 is added to 4.4 µM human ACC2. (b) The compound-induced shift (triangles) in the midpoint of the CD thermal transition of ACC2 (circles) is retained when seven residues are truncated but lost when 17 residues are truncated from the C-terminus. ACC2 was at 4–7 µM and where indicated CP-640188 was present at 33–50 µM. Lines are drawn only to indicate trends. (c) Multiple compounds induce a titratable melting-temperature shift in ACC2 (1693–2451). ACC2 at 1–2 µM was titrated with 0–10 µM CP-640188 (circles), GSK723A (squares) and GSK193A (triangles) and subjected to thermal denaturation in the presence of (1×) SYPRO Orange fluorescent dye. The resulting T m values from fitted curves are plotted against compound concentration.