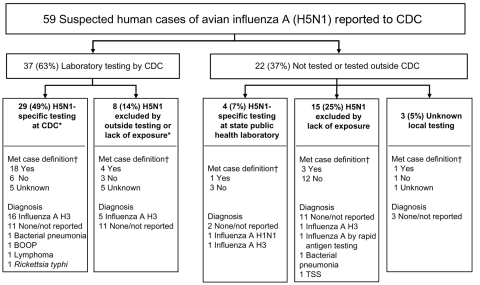
Figure.
Influenza testing of suspected US cases of avian influenza A H5N1 reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) from February 2003 through May 2006. *Of the 37 samples tested by CDC, 35 were respiratory samples, 1 was serum, and 1 was a lung specimen. All 35 respiratory samples received by CDC were tested for human influenza by reverse transcription–PCR, and the serum sample was tested by microneutralization assay. †CDC suspected H5N1 case definition, February 2, 2004–June 7, 2006 (6): a patient is hospitalized and has radiographically confirmed pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or other severe respiratory illness for which an alternate diagnosis has not been established; and the patient has a history of travel within 10 days of symptom onset to a country with documented H5N1 avian influenza in poultry and/or humans; or a patient is hospitalized or ambulatory and has a documented temperature >38°C (>100.4°F); and has a cough, sore throat, or shortness of breath; and has a history of contact with domestic poultry or a patient with known or suspected H5N1 case in an H5N1-affected country <10 days of symptom onset. BOOP, bronchiolitis and obliterans organizing pneumonia; TSS, toxic shock syndrome.