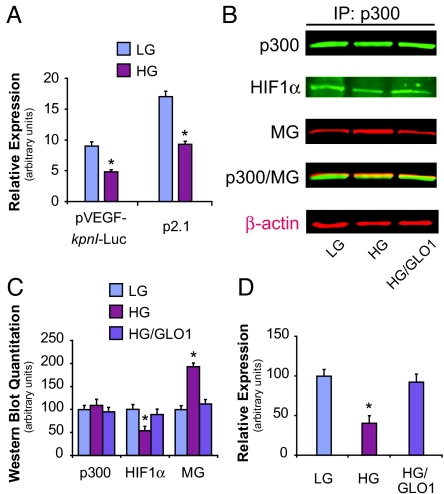
Fig. 2.
Hyperglycemia-induced impairment in HIF-1 transactivation occurs as a result of decreased HIF-1α binding to p300. (A) Plasmids containing a full-length VEGF-A promoter (pVEGF-kpnI-luc) or the hypoxia response element for the enolase gene (p2.1), both linked to firefly luciferase, were transfected into cells and subsequently exposed to hypoxia. HG exposure decreased HIF-1 transactivation with use of either plasmid. (B) HAECs were treated for 5 days with LG, HG, or HG after infection of GLO1 adenovirus (HG/GLO1). After exposure to hypoxia for 18 h, cell lysates were collected for immunoprecipitation (IP) of p300 and subsequently immunoblotted (IB) for p300, methylglyoxal (MG), or HIF-1α. β-actin was used as an input control (shown in red typeface). (C) Western blot quantitation of panel B. (D) HAECs were transfected with plasmids containing the HIF-1α-CAD and the p300-CH1 domain together with a reporter plasmid containing a Gal4-binding motif upstream of a firefly luciferase reporter gene. Cells were grown in LG or HG and exposed to normoxia or hypoxia, and the level of luciferase reporter activity subsequently measured. Impaired HIF-1α/p300 binding in HG was completely reversed with GLO1 treatment. *, P < 0.05 vs. LG group. n = 3.