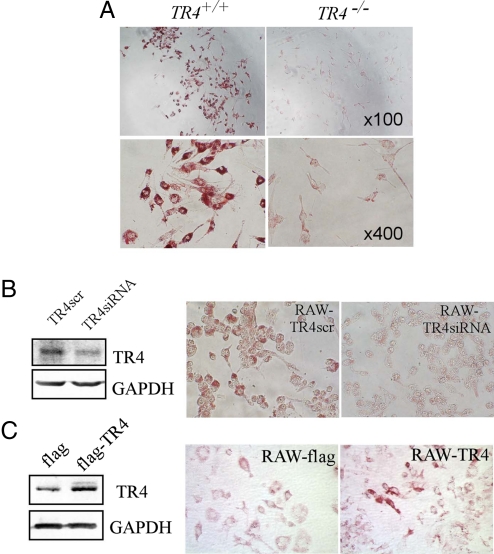
Fig. 1.
TR4 modulates foam cell formation. (A) Foam cell formation is decreased in TR4−/− macrophages. Thioglycolate-stimulated peritoneal macrophages from TR4+/+ mice and TR4−/− mice were seeded on a 96-well plate and exposed to 100 μg/mL oxLDL for 24 h. Oil red O staining was performed as described in Materials and Methods. Cells containing oil red O-positive fat droplets were considered foam cells. (B) Knockdown of TR4 in macrophage RAW264.7 cells (RAW-TR4-siRNA) reduces foam cell formation. RAW264.7 cells were infected with retrovirus expressing TR4-siRNA or control TR4-scramble. After selection with puromycin (5 μg/mL) for 3 days, the cells were harvested and TR4 expression levels were examined by Western blot analysis (Left). (Right) RAW-TR4siRNA cells and their empty vector control cells were treated with 100 μg/mL oxLDL for 24 h. Oil red O staining was performed as above. (C) Overexpression of TR4 in macrophage RAW264.7 cells (RAW-TR4) induces foam cell formation. RAW264.7 cells were stably transfected with pCDNA3-flag-TR4 or empty vector pCDNA3-flag. After selection with G418 (500 μg/mL) for 2 weeks, the stable cells were harvested and TR4 protein expression was examined by Western blot analysis. GAPDH served as the loading control (Left). (Right) RAW-TR4 cells and their empty vector control cells were treated with 8 μg/mL oxLDL for 24 h. Oil red O staining was performed as described in Materials and Methods.