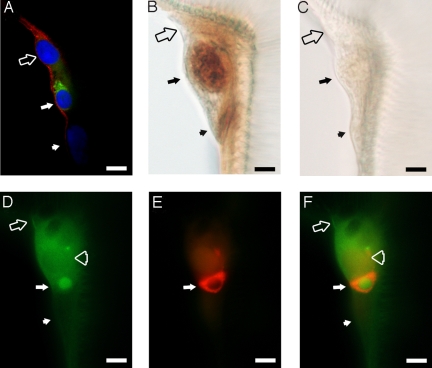
Fig. 4.
BdmGC-1 is colocalized with ETH1 and cGMP in epitracheal glands. Epitracheal glands from third instar larvae before pupal ecdysis were used for immuno-visualization. (A) Immuno-visualization of epitracheal gland by confocal microscopy. BdmGC-1 (red color; labeled by N-terminal-specific antibodies) shows cell surface expression and ETH-1 (green color) is localized in the cytoplasm of the Inka cell. The tissue is counterstained with DAPI (blue color). (B) To verify that Inka cells of B. dorsalis respond to EH by producing cGMP, tracheae of larvae were dissected and treated with 200 pM EH, then labeled with cGMP-specific antibodies and visualized by HRP/DAB. (C) Tracheae were treated with PBS instead of EH, followed by cGMP antibody labeling. (D and E) Epitracheal gland labeled by BdmGC-1 C-terminal specific (green color) antibodies and ETH1-(red color) antibodies, respectively. (F) Merged image of (E and F). Filled arrow: Inka cell, filled arrowhead: canal cell, open arrow: cell lying atop of epitracheal gland, and open arrowhead: cell adjacent to Inka cell. (Scale bars, 10 μm.)