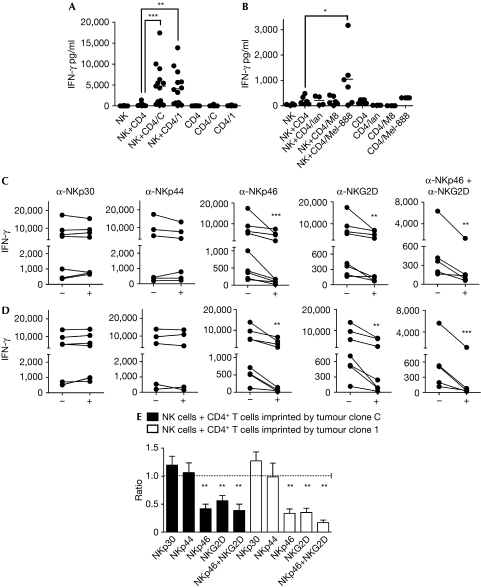
Figure 2.
Interferon-γ secretion by natural killer cells. The experimental approach is detailed in Supplementary Fig 1B online. (A,B) Natural killer (NK), cells alone; NK+CD4, NK cells co-cultured with CD4 T cells that did not contact tumour cells; NK+CD4/C, NK+CD4/1, NK+CD4/Ian, NK+CD4/M8 and NK+CD4/Mel-888, NK cells co-cultured with CD4 T cells previously co-cultured with tumour clone C or tumour clone 1, or IIB-MEL-IAN, M8 or Mel-888 cells, respectively. CD4, CD4/C, CD4/1, CD4/Ian, CD4/M8 and CD4/Mel-888, CD4+ T cells cultured in the absence or in the presence of tumour clone C or 1, or IIB-MEL-IAN, M8 or Mel-888 cells, respectively. For blocking experiments, NK cells were co-cultured with CD4+ T cells imprinted by tumour clone C (C) or tumour clone 1 (D), in the absence (−) or in the presence (+) of the indicated blocking monoclonal antibodies. Each dot or line in (A–D) represents the result obtained with cells from a different donor. To circumvent the heterogeneity commonly observed in IFN-γ secretion among different donors, the ratio of IFN-γ secretion observed in the presence to that obtained in the absence of the blocking monoclonal antibodies is shown (E). The mean±s.e.m. obtained in independent experiments carried out with cells from five to eight different donors is shown. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. IFN-γ, interferon-γ.