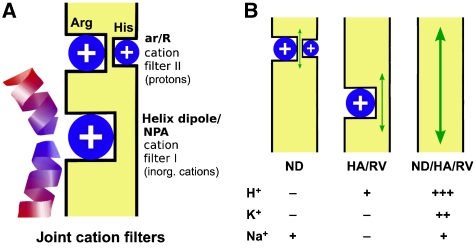
Figure 5.
Model of the AQP joint cation filters. (A) The primordial AQPs already selected against inorganic cations, such as Na+ and K+, because of a positive electrostatic field from the helix dipols and the lack of cation coordination sites in the NPA region (filter I); yet, protons leaked through. Later, a second cation filter evolved in the ar/R region, which fully excluded protons (filter II) and provided individual selectivity properties for water, glycerol, urea, and ammonia. (B) Disturbance of the filter regions by point mutations leads to Na+ leakage as was the case for the AQP1-N192D mutant (ND; exchange of asparagine for aspartate in the NPA region), enables low proton permeability (HA/RV; removal of positive charges in the ar/R region) or switches the AQP into a cation channel (ND/HA/RV; combination of the NPA and ar/R mutations).