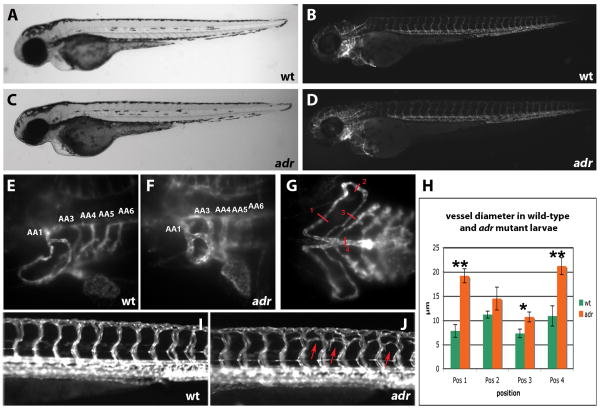
Figure 1.
(A-G) Bright-field (A and C), epifluorescence (B and D) and SPIM (E - G) micrographs of 80hpf wild-type (A, B, E, and G) and adrs277 mutant (C, D, and F) Tg(flk1:EGFP)s843 larvae, shown in lateral (A to F) and ventral (G) views. At this stage, the mutants resemble their wild-type siblings except for the dilatation of the aortic arch vessels (numbered AA1-6, the vestigial AA243 is not visible).
(H) Diagram showing the diameter of the aortic arch vessels in wild-type (n = 4) and adrs277 mutant (n = 4) larvae measured at the positions indicated in G. Error bars show the standard deviation. The P value was considered statistically significant and marked by ** when (P< 0.01) and by * when (P< 0.05).
(I, J) Epifluorescence micrographs of 82hpf wild-type (I) and adrs277 mutant (J) Tg(flk1:EGFP)s843 larvae shown in lateral views. The intersomitic vessels in adr mutants exhibit ectopic branching (indicated by red arrows), especially in the dorsal half of the myotome.