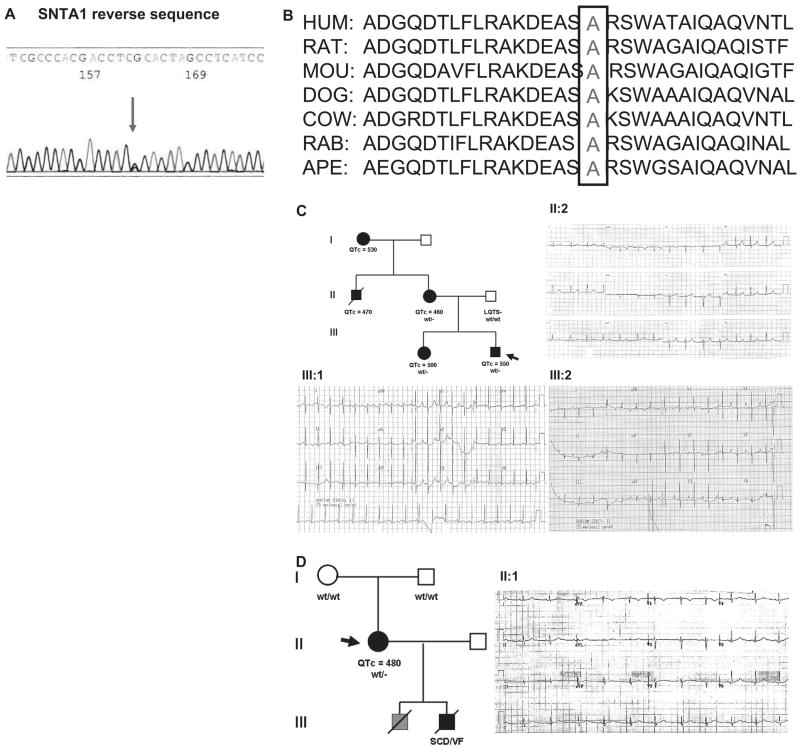
Figure 1.
The cytoskeletal protein syntrophin α1 (SNTA1) mutational analysis in long-QT syndrome (LQTS). Sequencing analysis demonstrates a novel nucleotide variant in SNTA1 leading to a nonsynonymous change in 3 patients (A) and amino acid conservation analysis of the A257G-SNTA1 variant (B), which modifies a highly conserved amino acid in SNTA1. C, LQT-249 family pedigree and ECG recording showing a pattern with features similar to LQT3 and a prolonged QT interval in proband III: 2, his sister III:1 and his mother II:2 bearing the A257G-SNTA1 mutation. The ECG of the proband demonstrates a prolonged QT interval and late onset T wave.19 D, LQT-682 family pedigree and ECG recording showing a pattern with features similar to LQT3 and a prolonged QT interval in proband II: 1 bearing the A257G-SNTA1 mutation.