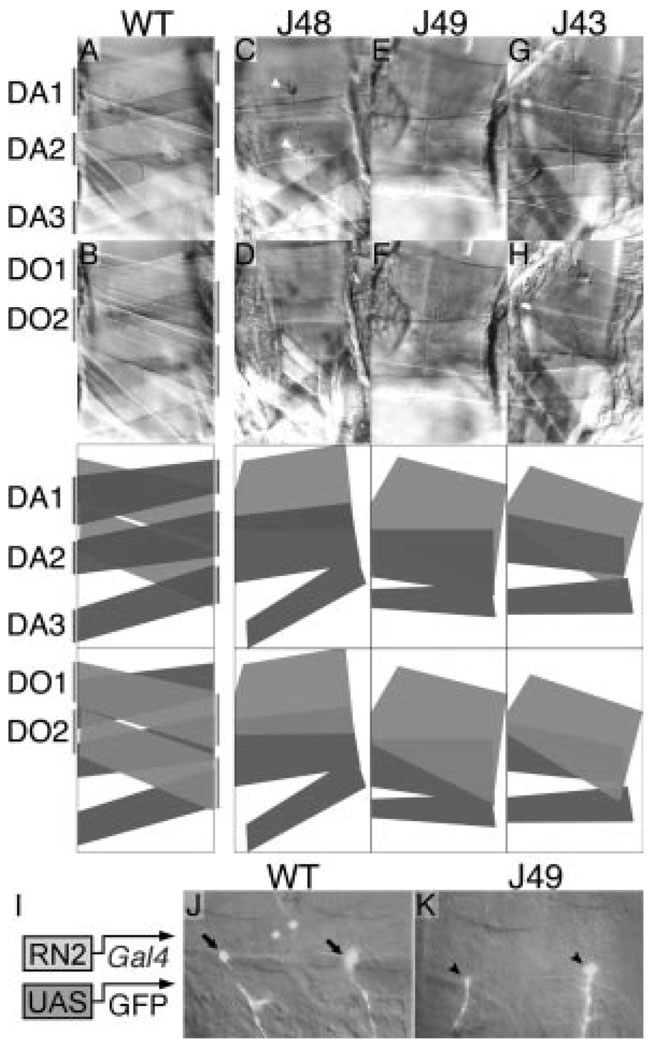
Figure 3.
Muscle defects and innervation by eve-expressing neurons in eve meso− larvae. Either wild-type (A and B) or eve meso− (C through H) third instar larvae were dissected to reveal the dorsal musculature (anterior is to the left, dorsal up). Three meso− lines are shown, each null mutant for eve and rescued by the indicated eme-deleted transgene (J48 in C and D; J49 in E and F; J43 in G and H). Each panel in the second row shows the same embryo as that above it. The focal plane in the top row is that of the normal DA1, DA2, and DA3, whereas the focal plane in the second row is that of the normal DO1 and DO2. The muscle pattern in each pair of panels is diagrammed in the 2 panels directly below them, with dark gray representing muscles in the DA1,2,3 focal plane and light gray representing muscles in the DO1,2 focal plane. Note in the meso− embryos the absence of a muscle in the normal DA1 position, the wider-than-normal muscle in the DA2 position, and the single muscle occupying most of the normal DO1,2 region. A similar range of phenotypes as that shown, including the particular variations in muscle widths, is seen in each of the meso− lines. Note also the innervation of both of the abnormal muscles in C, as evidenced by the tree-like branching structures of boutons (white arrowheads; visualized by anti-fasciclin II staining). I, Transgenes used to label the eve-expressing neurons (RP2 and aCC) that innervate DA1 and DO1. The mesodermal regulatory element derived from the eve gene (RN2-Gal4)22 drives expression of the Gal4 activator in the RP2 and aCC motorneurons (as well as in the interneuron pCC), which in turn activates the UAS-GFP reporter transgene. J and K, GFP image of a 2 segment-wide swath of a late stage 16 embryo is overlayed with the corresponding visible light image. J, Wild type; note the bulbous synapse at a point where DA1 and DO1 intersect on their ventral side (arrows). K, J49 eve meso−; note the innervation (arrowheads) at a point of intersection of the two remaining muscles described above.