Figure 3.
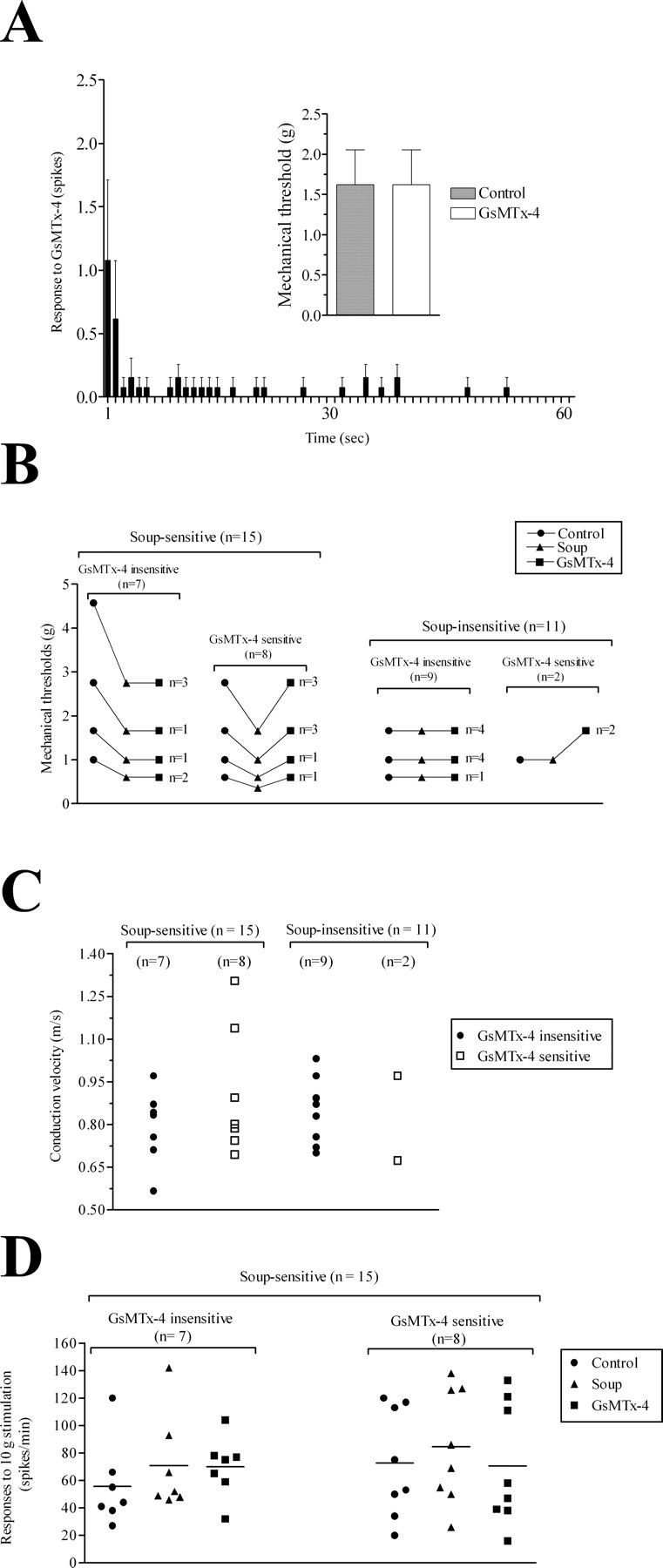
GsMTx-4 reverses the decrease in mechanical threshold induced by inflammatory soup in half of sensitized C-fibers. A, Intradermal injection of GsMTx-4 (1000 ng, 2.5 μl) adjacent to mechanical receptive fields did not induce significant activity in C-fibers. Inset, Mechanical thresholds of C-fibers were not significantly different from baseline after intradermal injection of GsMTx-4 (n = 13). B, Response of individual C-fibers to sustained (60 s) threshold mechanical stimulation before (●) and after (▴) intradermal injection of PGE2 and 5-HT and after a subsequent intradermal injection of GsMTx-4 (■). n is the number of fibers recorded. Injection of simplified inflammatory soup (PGE2 and 5-HT, 100 ng each) into the mechanical receptive field of C-fibers reduced the mechanical threshold in 15 of 26 C-fibers. A subsequent injection of GsMTx-4 (1000 ng, 2.5 μl) into the mechanical receptive field of a C-fiber reversed the decrease in mechanical thresholds induced by simplified soup in 50% of the sensitized C-fibers (8 of 15). C, There is no significant difference in the conduction velocity between C-fibers that were soup sensitive (n = 15) vs soup insensitive (n = 11) or between C-fibers that were GsMTx-4 sensitive or GsMTx-4 insensitive (p > 0.05, Tukey's post hoc multiple comparison test). D, Response of sensitized C-fibers to suprathreshold (10 g) mechanical stimulation before (●) and after (▴) intradermal injection of PGE2 and 5-HT and after a subsequent intradermal injection of GsMTx-4 (■). There was no significant difference between C-fibers that were GsMTx-4-sensitive or GsMTx-4-insensitive.
