Fig. 1.
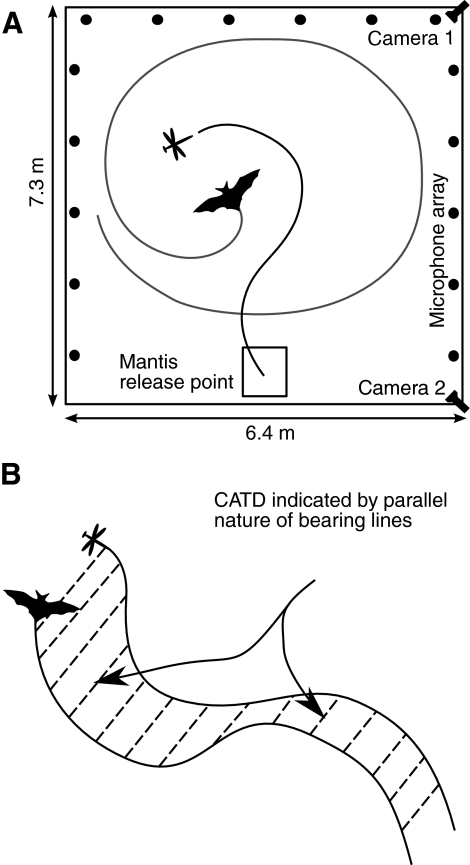
(A) Schematic of instrumented flight room. The flight room was illuminated with red wavelength lighting. Two high speed infra-red cameras recorded the flights of the bat and mantis. Two ultrasonic microphones placed in the middle of the flight room, 30 cm above the floor, were used to record the vocalizations of the bat. An array of 16 microphones placed round the room was used to record sonar beam patterns emitted by the bats. The mantis was released from the indicated position, from a height of 2 m. (B) Graphical illustration of constant absolute target direction (CATD) pursuit. The bat adopts a CATD strategy if bearing lines drawn to the target appear parallel in the world (absolute) reference frame. Under this condition the bearing angle can change, but the absolute direction of the bearing vector does not. A pursuit trajectory that maintains CATD minimizes (on average) time to intercept of an unpredictably moving target (Ghose et al., 2006).