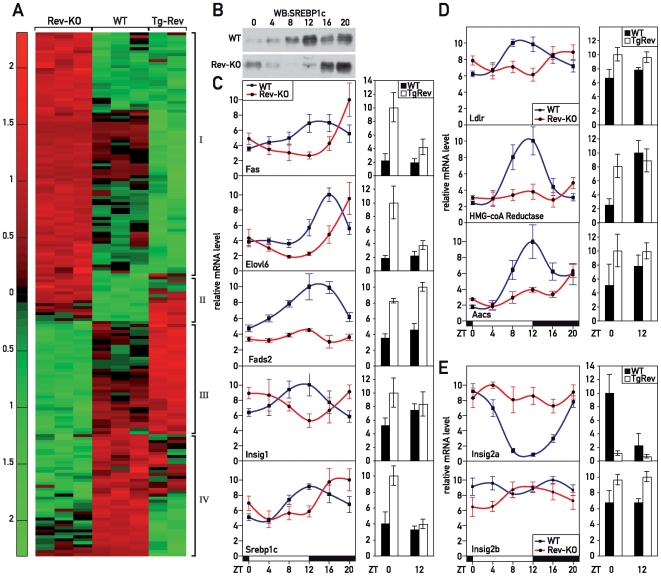
Figure 1. REV-ERBα controls the temporal nuclear accumulation of SREBP and the transcription of SREBP target genes.
(A) Affymetrix-microarray analysis of liver RNA from mice of various genotypes. The heat map displays transcripts with differential accumulation in WT, Rev-KO, and TgRev mice. Differentially expressed transcripts of mice with different genotypes are clustered into four classes: class I: Rev-KO>WT≥TgRev; class II: Rev-KO>WT<TgRev; class III: Rev-KO<WT≤TgRev; class IV: Rev-KO<WT>TgRev (see also Figure S2). (B) Temporal accumulation of SREBP1c in liver nuclear extract. (C) Temporal expression of transcripts from selected SREBP1c genes. (D) Temporal expression of transcripts from selected SREBP2 target genes. (E) Temporal expression of Insig2 transcripts. The data displayed in (C–E) were obtained by quantitative (Q) RT-PCR experiments on whole-cell liver RNA from WT, Rev-KO, and TgRev animals. The data represent the mean±SEM (n = 4–6).