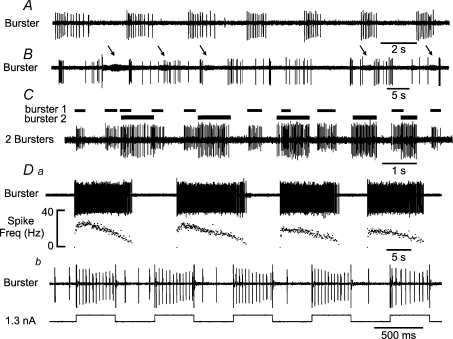
Figure 7. Examples of discharge of three burster neurones recorded from the medulla following a blockade of fast synaptic transmission.
Note the different frequencies of discharge of the three burster neurones (A–D). In B, there is a second burster in the background (arrowed). In C, two bursters were recorded simultaneously from a single microelectrode; note their different firing rates and patterns indicating that synaptic transmission was blocked. Horizontal bars indicate the duration of the bursts of each neurone. In Da, the firing pattern was of a decrementing type, a typical feature of medullary bursters with long discharge duration. In detail, the initial period of neuronal discharge was very steeply augmenting, followed by a brief plateau and then a rate of decline that was much slower than the initial rate of rise. The neurone was entrained by applying current pulses in an attempt to label the neurone juxtacellularly by iontophoretic injection of biotinamide (Db).