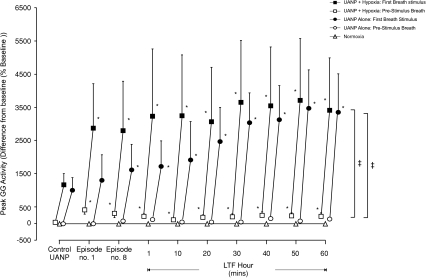
Figure 3. Group mean (±s.e.m., n= 8) effect of repeated exposure to upper airway negative pressure (UANP) and/or hypoxia on peak genioglossus muscle activity in anaesthetized spontaneously breathing rats.
The mean change in pre-stimulus (open symbols) and first-breath (filled symbols) peak genioglossus (GG) muscle activity expressed as a percentage of baseline in response to UANP stimulation alone under control conditions (average of 5 UANP stimuli), during the first (no. 1) and last (no. 8) of eight repeated episodes of UANP alone (circles), UANP together with hypoxia (squares) and normoxia alone (triangles, no pressure applied), and to single pulses of UANP alone delivered at separate time points over the subsequent hour. *Significant change in peak GG activity from control pressure responses (P < 0.05). ‡Significant difference from pre-stimulus breath activity. LTF, long-term facilitation.