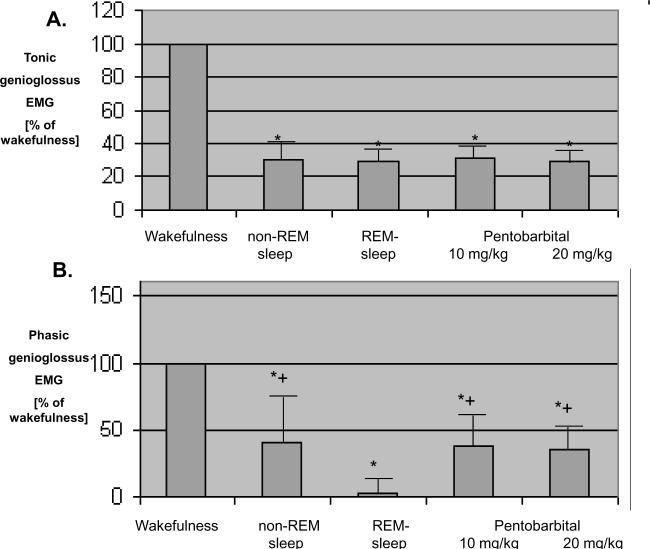
Figure 6.
Comparison of the effects of pentobarbital and normal sleep on genioglossus muscle activity in chronically instrumented rats. Means ± SEM.
A. Nadir tonic (non-respiratory) genioglossus muscle activity during wakefulness, sleep, and pentobarbital anesthesia. Compared to wakefulness activity, nadir genioglossus activity is significantly lower during sleep and pentobarbital anesthesia, but values observed during pentobarbital anesthesia did not differ from those observed during non REM and REM sleep. *p<0.05 versus wakefulness.
B. Phasic (respiratory) genioglossus activity during wakefulness, sleep, and pentobarbital anesthesia. Compared to wakefulness activity, phasic genioglossus activity was significantly lower during sleep and pentobarbital anesthesia. Phasic (respiratory) genioglossus activity during REM-sleep was significantly lower compared to non-REM sleep and pentobarbital anesthesia at a dose-level of 10 mg/kg.
REM=rapid-eye-movement, EMG=electromyogram.