3.
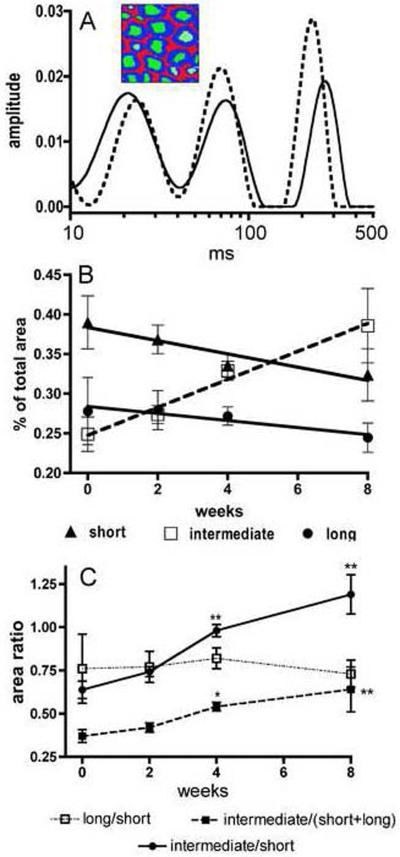
Multi-exponential transverse relaxation (MET2) analyses of sciatic nerve showing the relative quantities of protons within three water pools as a function of dithiocarbamate exposure duration. (A) Two representative spectra of sciatic nerve water T2 relaxation times are shown illustrating three peaks corresponding to three pools of water protons. The inset illustrates the myelin (blue), axoplasm (green), and extra-cellular (red) water pools attributed to these three relaxation components. The spectrum obtained from a 4 week DEDC exposed animal (dotted line) presents a relative decrease in the contribution to total peak area for the short T2 component relative to that observed in the control spectrum (solid line). (B) Changes in the contribution of each T2 relaxation component are shown as a function of DEDC exposure. All three components demonstrated significant correlations to exposure duration (short component p < 0.05, r2 = 0.89; long component p < 0.05, r2 = 0.87; and intermediate component p < 0.01, r2 = 0.98 as determined by the Pearson correlation test n=4). The intermediate component contribution was positively correlated and the short and long components' contributions negatively correlated with increasing exposure duration. (C) The ratios of individual component contribution to total peak area as a function of exposure duration are shown. The ratios of the intermediate component/short component and the intermediate component/(short + long) components increased with longer exposure and were significantly elevated relative to controls at the 4 and 8 week time points (* p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA and Dunnett's post hoc test n=4).