Fig. 2.
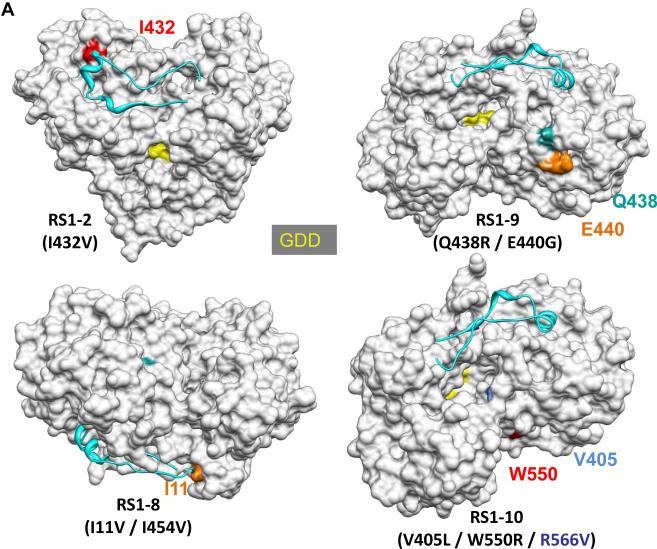
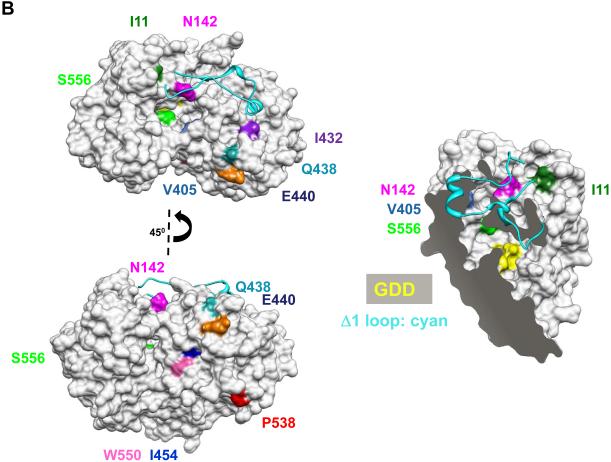
Locations of the mutations in NS5B that conferred resistance to CsA. (A) Models of the mutations in NS5B from RS1-2, RS1-8, RS1-9, and RS1-10. The structure of the NS5B protein is from Ago et al. (16) (pdb: 1QUV). Several features in the structures serve as landmarks. The Δ1 loop that extends from the thumb to the finger subdomains is colored cyan. The GDD residues that coordinate divalent metals for catalysis are shown in yellow. Note that the active site within the enclosed template channel was obscured in some views. The back of the template channel includes a concave surface, the location of several of the mutations. (B) CsA mutations exist in two regions within the NS5B protein. The mutations include those identified in this study and the two from Fernandes et al. (15), which also conferred resistance to CsA; and the mutation N142S from Wiedmann et al. (34). The first region is in or near the template channel (I11, N142, V405, I432, and S556) and the second is within one face of the concave surface (Q438, E440, I454, P538, and W550). A cut-away view of the molecule is shown to allow visualization of the mutations in the template channel.