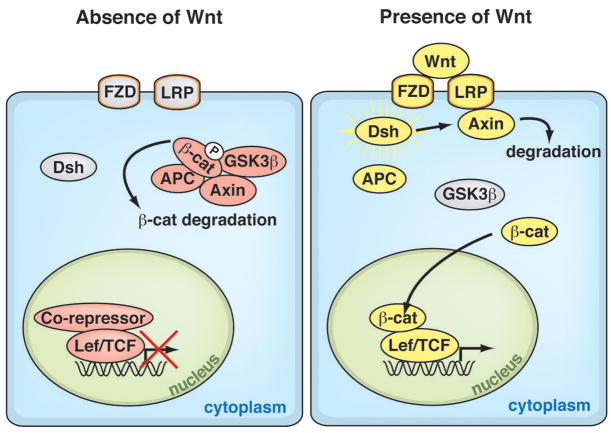
Figure 1. The Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.
Canonical Wnt signaling is initiated when Wnts bind to their cognate receptor complex of the transmembrane proteins Frizzled and Lrp. This interaction activates the cytoplasmic protein Dishevelled, which stabilizes β-catenin by inhibiting the kinase activity of the destruction complex of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), Axin, and glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β). Unphosphorylated β-catenin on its N-terminus translocates into the nucleus, where it interacts with the TCF/lymphoid enhancer factor (LEF) transcription factors to activate Wnt target genes. In the absence of Wnt, the destruction complex phosphorylates β-catenin, targeting it for degradation.