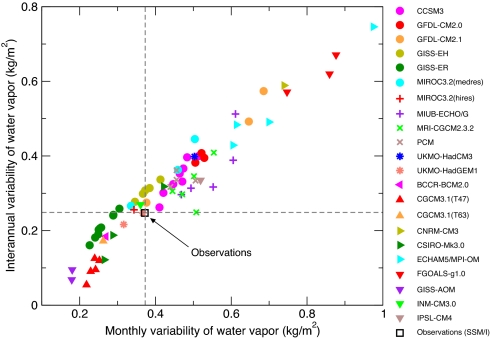
Fig. 1.
Comparison of the simulated and observed temporal variability of atmospheric water vapor. Observations are from the SSM/I dataset (25, 26); model data are from 71 realizations of 20th century climate change performed with 22 different models (see SI Appendix). All variability calculations rely on monthly mean values of 〈W〉, the spatial average of total atmospheric moisture over near-global oceans. Model and observational 〈W〉 data were first expressed as anomalies relative to climatological monthly means over the period 1988–1999 and then linearly detrended. We computed temporal standard deviations from both the unfiltered and filtered anomaly data. The latter were smoothed by using a filter with a half-power point at ≈2 years. The raw and filtered standard deviations provide information on monthly and interannual-timescale variability, respectively. All calculations were over the 144-month period from January 1988 to December 1999 (the period of maximum overlap between the SSM/I data and most 20CEN simulations). The dashed gray lines are centered on the observations.