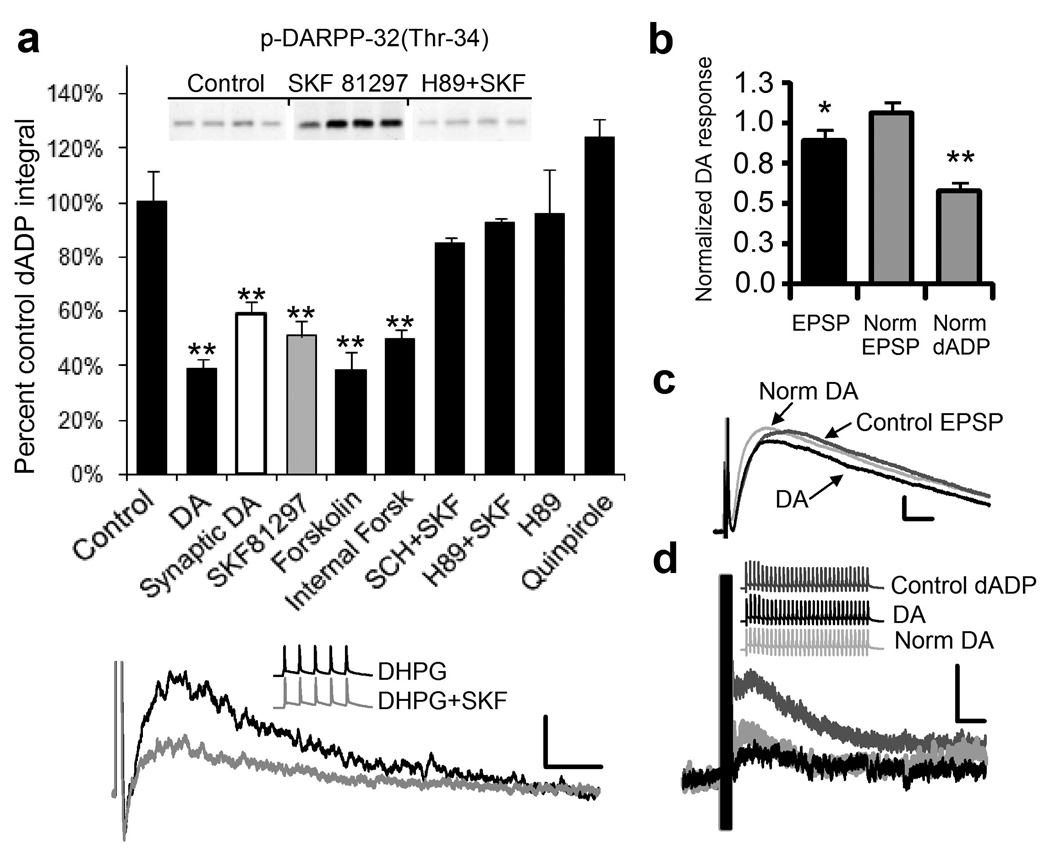
Figure 5.
Dopamine reduces the mGluR5/burst-induced dADP through a D1/5 receptor protein kinase A pathway. (a) Dopamine (DA; n=8;**p<0.01) reduces the DHPG-mediated burst-triggered dADP (Cont; n = 30) and the synaptically-triggered dADP (White Bar; n = 6; **p < 0.01). The D2 agonist, quinpirole (10 µM) fails to modulate the dADP (n = 8) while the D1R agonist, SKF81297 (10 µM; Gray bar) decreases the dADP (n = 28; **p < 0.002). Bath applied Forskolin (10 µM) reduced the DHPG-induced dADP (n = 8;**p<0.01) and Forskolin (10 µM) applied to the internal electrode solution reduced synaptically-triggered dADP (n=6;**p<0.01). The PKA inhibitor, H89 (10 µM) and the D1/5R antagonist, SCH 23390 (5 µM), blocked the D1/5R mediated inhibition. H89 alone (10 µM) had no effect (n = 6). The inset demonstrates the PKA inhibitor, H89, blocks the ability of SKF81297 to elevate PKA activity using an immunoblot for the PKA phosphorylation site of DARPP-32 (Thr 34) after incubating slices for 10 minutes in DHPG (50 µM;Cont) and SKF81297 (10 µM) or 1hour in H-89 (10 µM) prior to DHPG+SKF81297 (n = 4; *p < 0.05). (Bottom Panel) Superimposed representative traces showing the modulation of the DHPG (50 µM)-induced dADP by the D1/5R agonist SKF81297 (10 µM; Gray trace) compared to DHPG alone (Black trace). Scale bars of 2 mV and 2 s. Inset shows the 5 action potentials triggered by a 50 Hz train of brief current stimulation before and after DHPG or DHPG+ SKF81297. (b) Dopamine (DA; 10 µM) inhibits the synaptically-evoked (30 × 50 Hz) dADP (n = 5; **p < 0.01; right gray bar) more than the fast EPSP (n = 5;*p < 0.05; black bar) integral either before or after compensation for the reduced fast EPSP (Norm dADP). The middle gray bar shows the restored fast EPSP (Norm EPSP) in response to DA obtained by increasing the stimulation intensity. (c). Representative traces show the Control EPSP (Dark Gray) , the EPSP after DA (Black trace) or following compensation of the fast EPSP response by increasing the stimulus intensity back to the control level after DA (Norm DA; Light Gray trace). Scale bars show 2 mV and 5 ms. (d) Representative traces show the synaptically-triggered dADP control (Dark Gray Traces) and after DA (Black Traces) and after increasing the stimulus strength to restore the fast EPSP back to control levels (Light Gray Traces). Scale bars show 2 mV and 2 s