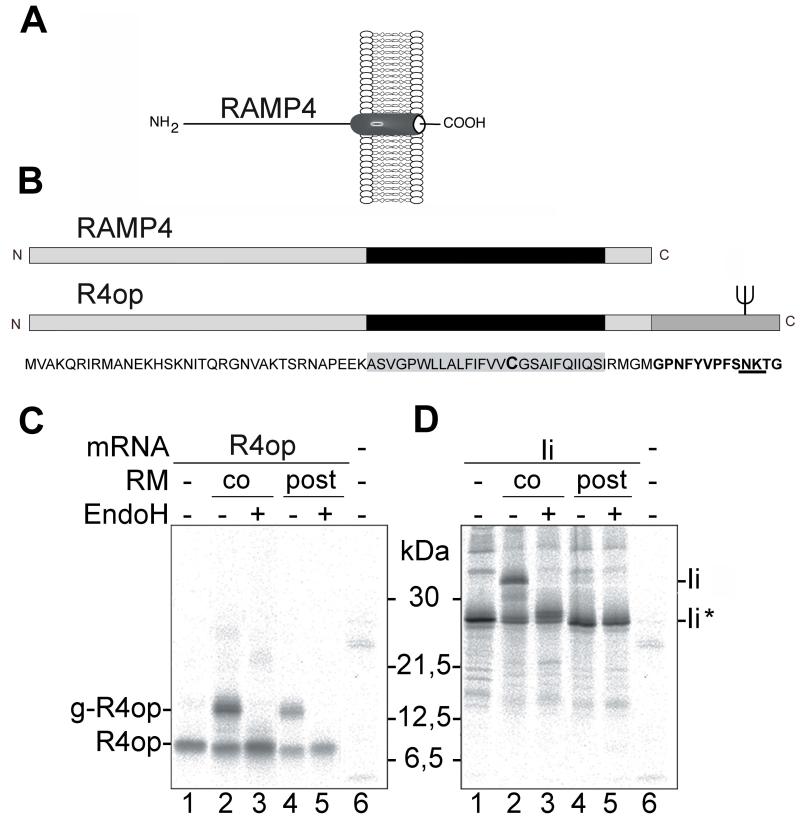
Fig. 1.
Posttranslational membrane insertion of R4op
(A) Topology of RAMP4 in the ER membrane. RAMP4 is a tail-anchored ER membrane protein that exposes its N-terminus on the cytosolic and the C-terminus on the lumenal side of the membrane. (B) Schematic representation of RAMP4 and RAMP4op (R4op). R4op contains at its C-terminus a bovine opsin tag comprising 13 amino acid residues (represented by a dark grey box). The tag provides an N-glycosylation site (fork). The predicted transmembrane domain (TMD) is represented as a black box. A single cysteine residue in the TMD is typed in bold. (C and D) In vitro translation and membrane insertion of R4op and the type II membrane protein Invariant chain (Ii) respectively. Proteins were synthesized in the rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL), in the absence (lanes 1, 4, 5 and 6) or presence of rough microsomes (RM co) (lanes 2 and 3). To samples shown in lanes 4 and 5, RM were added after completion of translation (RM post). Where indicated, samples were treated with EndoH to remove N-linked oligosaccharides. Proteins were immunoprecipitated using either anti-opsin (C) or anti-Ii (D) antibodies, separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. g-R4op: glycosylated R4op; Ii*: non-glycosylated Ii;