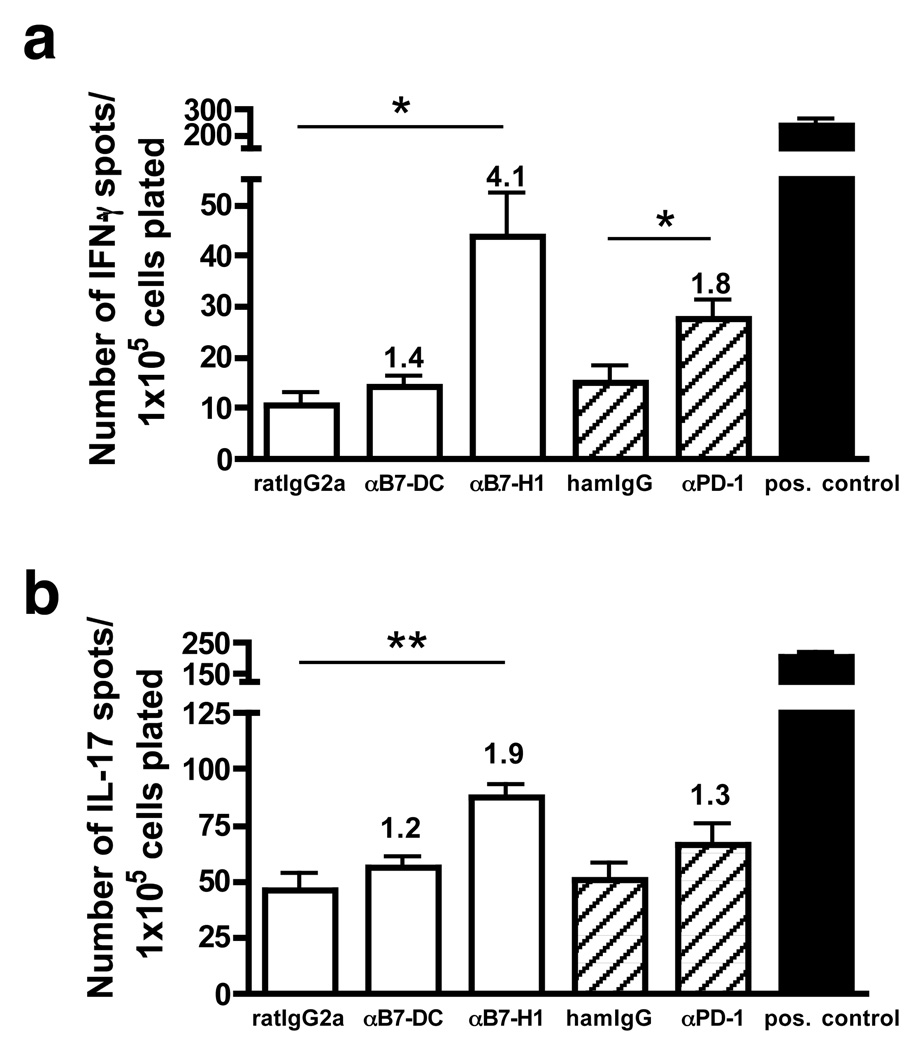
Figure 3.
Inhibition of acute phase-associated CNS T cells by B7-H1 and its receptor PD-1. The frequency of IFN-γ- (a) or IL-17-producing (b) T cells was determined by ELISPOT from the pooled CNS of PLP178–191-primed SJL mice (n=5–10) at the peak acute phase of R-EAE (day 14–15 PI). Endogenous presentation (in the absence of exogenously added PLP178–191 peptide) was determined in the presence of blocking anti-mouse B7-DC, B7-H1 (white bars) or PD-1 (hatched bars). Blocking/stimulatory indices, based on respective isotype controls, are shown above the bars. CNS cells incubated with anti-CD3 (black bars) were used as positive control. Data are representative of three (IL-17) or four (IFN-γ) separate experiments. Mean number of IL-17 or IFN-γ ELISPOTS significantly higher than isotype controls, **p< 0.01, *p< 0.05.