Figure 2.
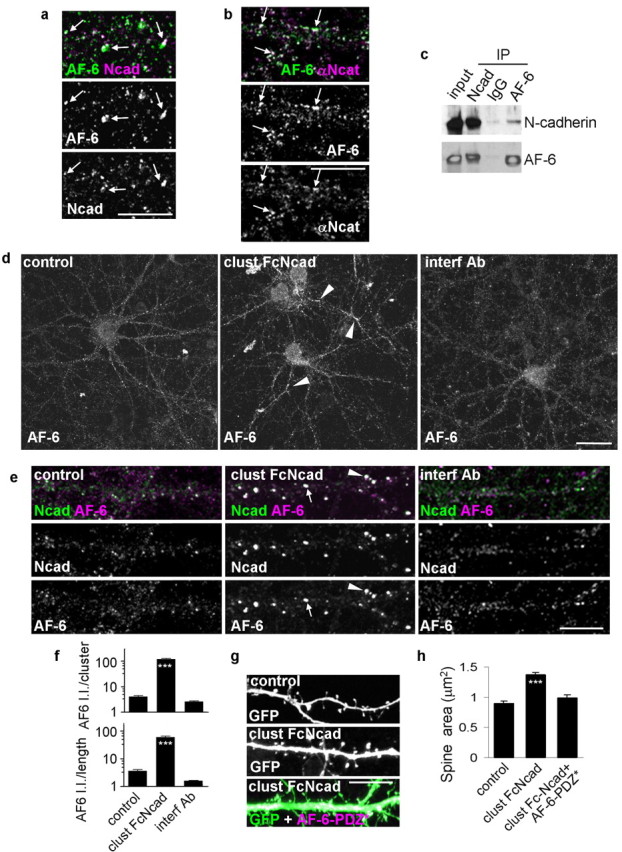
Activation and inhibition of N-cadherin adhesion result in AF-6 redistribution that underlies spine remodeling. a, AF-6 and N-cadherin colocalize in spines (arrows) in mature neurons (div 24–28). b, AF-6 and α-N-catenin colocalize at dendrite plasma membrane and in spines (arrows). c, AF-6 and N-cadherin coimmunoprecipitate from rat forebrain homogenate. d, N-cadherin activation or inhibition affects AF-6 localization in dendrites. The arrowheads indicate AF-6 clusters. e, Activation of N-cadherin adhesion induces formation of larger clusters of AF-6 along dendritic shafts (arrows) and in spines (arrowheads). f, Integrated intensities of AF-6 clusters that are colocalized with N-cadherin; quantification done for individual clusters and for all clusters within a segment of dendrite normalized to dendritic length. ***p < 0.001 compared with control and interf Ab. g, Spine enlargement induced by N-cadherin activation is blocked by expression of a mutant AF-6 with a nonfunctional PDZ domain (AF-6-PDZ*). h, Quantification of spine areas in g. ***p < 0.001 compared with control or clust FcNcad plus AF-6-PDZ*. Error bars indicate SEM. Scale bars: a, b, e, g, 10 μm; d, 30 μm.
